Are Nucleic Acids Monomers? Quick Facts & Insights.

Are nucleic acids monomers? This question often arises in biochemistry and molecular biology discussions. Nucleic acids, specifically DNA and RNA, are essential molecules that store and transmit genetic information. Understanding their structure is crucial for grasping their function. Let’s explore whether nucleic acids are monomers and uncover key facts and insights.
What Are Nucleic Acids?

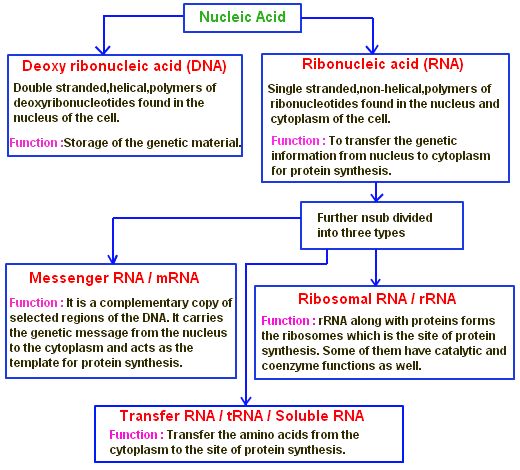
Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of smaller units called nucleotides. These molecules play a vital role in storing, transmitting, and expressing genetic information. The two primary types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Are Nucleic Acids Monomers?

Nucleic acids themselves are not monomers; they are polymers. Monomers are single units that combine to form larger molecules. In the case of nucleic acids, the monomers are nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of:
- A phosphate group
- A five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA)
- A nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine/uracil)
The Role of Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. When nucleotides link together through phosphodiester bonds, they form the backbone of DNA and RNA. This polymerization process creates the long, chain-like structure essential for genetic coding.
Key Differences: Monomers vs. Polymers
To clarify, here’s a comparison:
| Aspect | Monomers (Nucleotides) | Polymers (Nucleic Acids) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single units | Large molecules formed by monomers |
| Components | Phosphate, sugar, base | Multiple nucleotides linked together |
| Function | Building blocks | Store and transmit genetic information |

Quick Facts About Nucleic Acids

- DNA is double-stranded and forms a double helix structure.
- RNA is typically single-stranded and plays a key role in protein synthesis.
- Nucleic acids are found in all living organisms, from bacteria to humans.
- The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines an organism’s genetic traits.
📌 Note: Understanding the difference between monomers and polymers is essential for studying molecular biology and genetics.
Checklist: Nucleic Acids and Monomers

- Nucleic acids are polymers, not monomers.
- Nucleotides are the monomers of nucleic acids.
- Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base.
- DNA and RNA are the two primary types of nucleic acids.
Nucleic acids are fundamental to life, serving as the blueprint for all biological processes. While they are not monomers themselves, their structure relies on nucleotide monomers. By understanding this relationship, we gain insights into the intricate mechanisms of genetics and molecular biology.
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
+
The monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides, each consisting of a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
Are DNA and RNA polymers or monomers?
+
Both DNA and RNA are polymers formed by the linkage of nucleotide monomers.
What is the primary function of nucleic acids?
+
Nucleic acids primarily store, transmit, and express genetic information, essential for all living organisms.