How to Calculate Rectangle Area Moment of Inertia

Understanding the rectangle area moment of inertia is crucial for engineers, architects, and anyone working with structural mechanics. This property determines how a rectangular cross-section resists bending, making it essential in designing beams, bridges, and other load-bearing structures. Below, we’ll guide you through the step-by-step process of calculating the area moment of inertia for a rectangle, ensuring clarity and precision.
What is the Area Moment of Inertia?

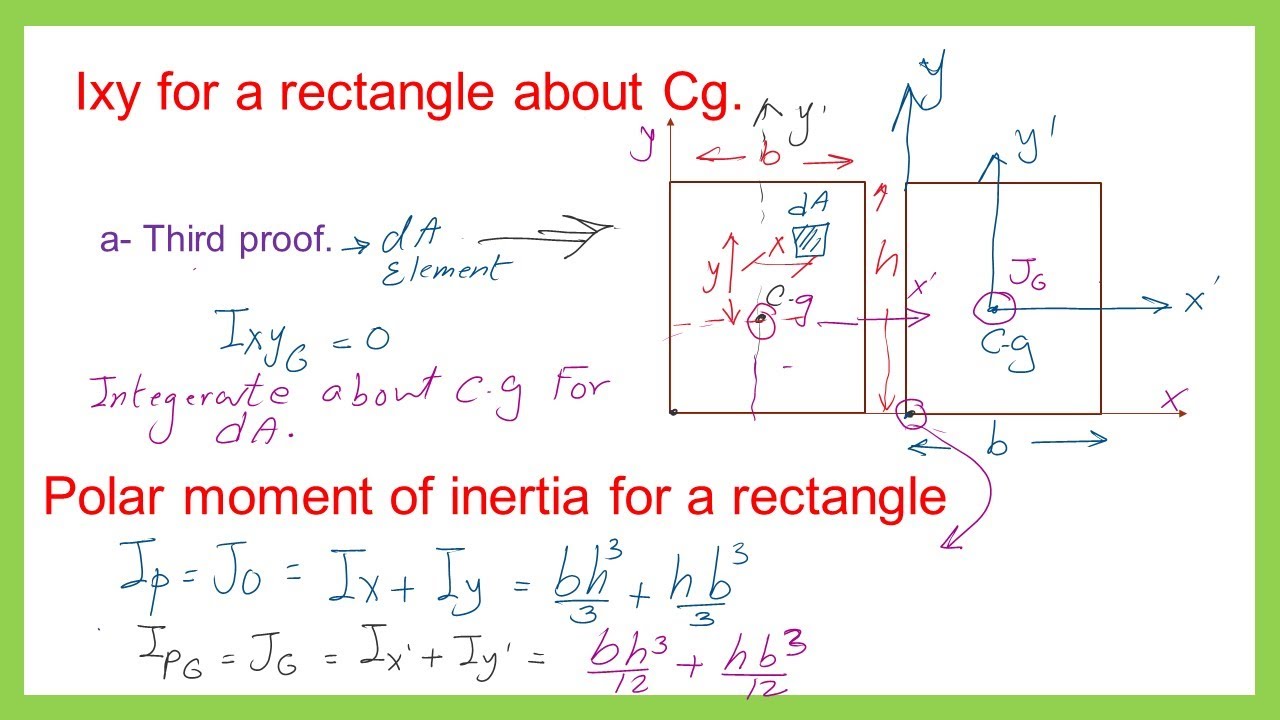
The area moment of inertia, often denoted as I, measures an object’s resistance to bending or deformation. For a rectangle, it depends on the dimensions: width (b) and height (h). The formula for a rectangle’s area moment of inertia about its centroidal axis is:
I = (1⁄12) × b × h³
This formula is fundamental for structural analysis, ensuring components can withstand applied loads without failing.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Rectangle Area Moment of Inertia

Step 1: Identify the Rectangle’s Dimensions
Before calculating, measure or determine the width (b) and height (h) of the rectangle. Accuracy in these measurements is critical for precise results.
Step 2: Apply the Formula
Use the formula I = (1⁄12) × b × h³ to compute the area moment of inertia. Ensure units are consistent (e.g., both dimensions in millimeters or inches).
📘 Note: Always verify the units of measurement to avoid calculation errors.
Step 3: Interpret the Results
A higher area moment of inertia indicates greater resistance to bending. This value is vital for material selection and structural design.
Practical Applications of Rectangle Area Moment of Inertia

- Structural Engineering: Designing beams and columns to withstand loads.
- Mechanical Engineering: Analyzing stress distribution in rectangular components.
- Architecture: Ensuring building elements are structurally sound.
Checklist for Calculating Rectangle Area Moment of Inertia
- Measure width (b) and height (h) accurately.
- Use the formula I = (1⁄12) × b × h³.
- Verify units for consistency.
- Apply the result to structural or mechanical analysis.
What is the area moment of inertia for a rectangle?
+The area moment of inertia for a rectangle is calculated using the formula I = (1/12) × b × h³, where b is the width and h is the height.
Why is the area moment of inertia important?
+It determines a structure’s resistance to bending, ensuring safety and stability in engineering and architectural designs.
Can the area moment of inertia be zero?
+No, the area moment of inertia cannot be zero for a rectangle unless one of its dimensions is zero, which is not practical.
Mastering the calculation of the rectangle area moment of inertia is essential for professionals in engineering and architecture. By following the steps outlined above, you can accurately determine this critical property, ensuring the structural integrity of your projects. Remember, precision in measurements and consistent units are key to reliable results.
Related Keywords: area moment of inertia calculator, moment of inertia formula, structural engineering basics, beam design principles.



