Exploring Blood Cells Under the Microscope

<!DOCTYPE html>
Have you ever wondered what blood cells look like up close? Exploring blood cells under the microscope is a fascinating journey into the microscopic world of our circulatory system. Whether you're a student, a medical professional, or simply curious, observing blood cells can reveal intricate details about their structure and function. From red blood cells (RBCs) to white blood cells (WBCs) and platelets, each component plays a vital role in maintaining health. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of preparing and examining blood samples, highlight key features to look for, and provide tips for achieving the best results. (blood cell microscopy, red blood cells, white blood cells)
Essential Tools for Blood Cell Microscopy

Before diving into the microscopic exploration, it’s crucial to gather the right tools. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Microscope: A compound microscope with at least 400x magnification is ideal for observing blood cells.
- Slides and Cover Slips: Clean glass slides and cover slips to hold the blood sample.
- Stain Solutions: Common stains like Wright’s or Giemsa enhance cell visibility and differentiation.
- Pipettes and Droppers: For precise handling of blood and staining solutions.
- Blood Sample: A small drop of blood, typically from a finger prick, is sufficient for examination.
📌 Note: Always handle blood samples with care and follow safety protocols to prevent contamination.
Step-by-Step Guide to Preparing a Blood Smear

Creating a proper blood smear is essential for clear microscopic observation. Follow these steps:
- Clean the Slide: Ensure the glass slide is free of dust and debris.
- Apply the Blood Sample: Place a small drop of blood near one end of the slide.
- Spread the Sample: Use a second slide to gently spread the blood into a thin, even layer.
- Air Dry: Allow the smear to air dry completely before staining.
- Fix the Sample: Fix the smear by gently passing it through a flame or using a fixative solution.
- Stain the Sample: Apply the chosen stain and let it sit for the recommended time before rinsing and drying.
📌 Note: Over-staining can obscure cell details, so follow staining instructions carefully.
Identifying Blood Cells Under the Microscope
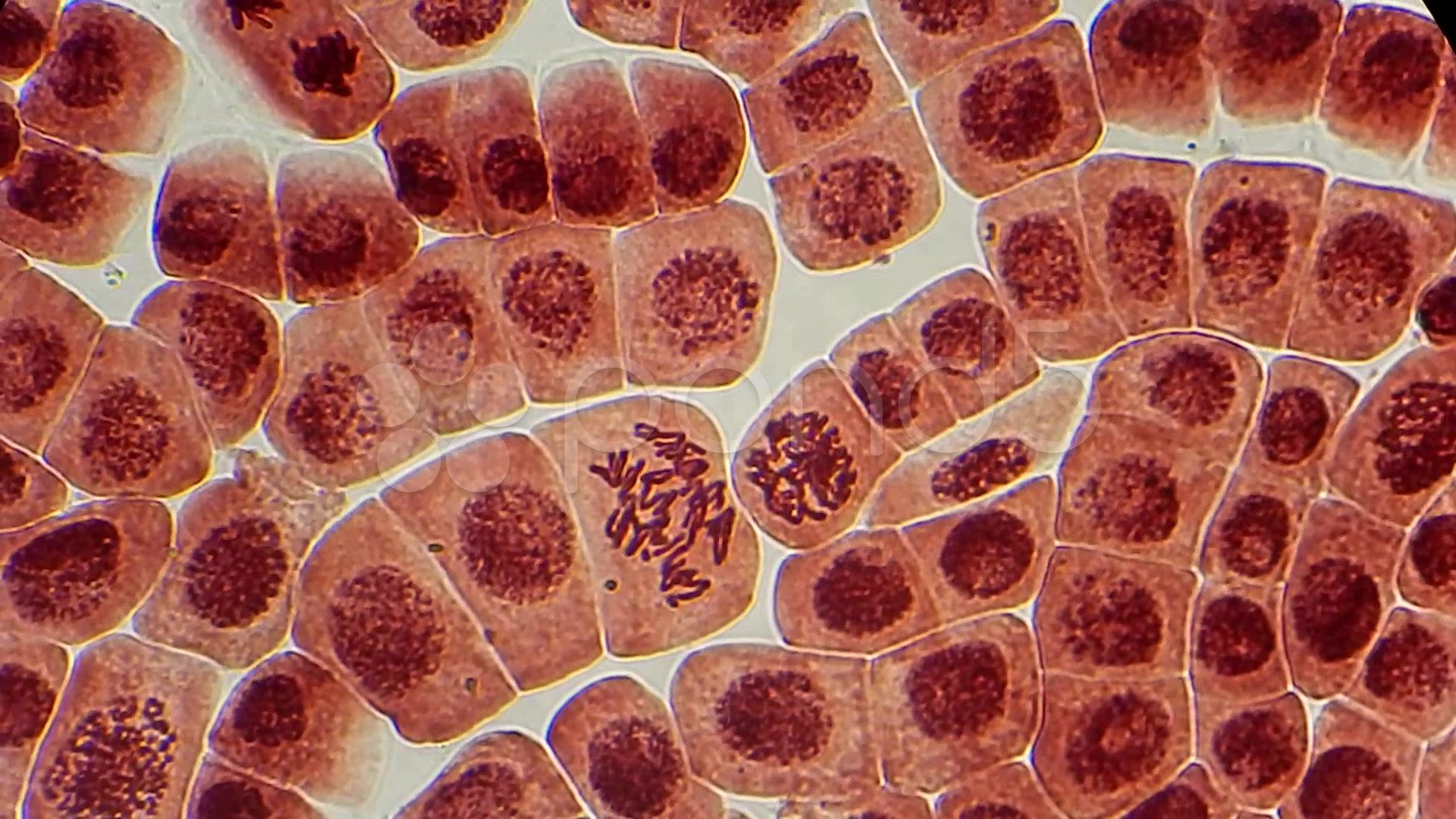
Once your sample is prepared, it’s time to examine it under the microscope. Here’s what to look for:
| Cell Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Red Blood Cells (RBCs) | Biconcave, disc-shaped, no nucleus, appears pink/red under stain. |
| White Blood Cells (WBCs) | Larger than RBCs, with a nucleus, appears blue/purple under stain. |
| Platelets | Small, irregular shapes, often seen in clusters. |

Observing these cells can provide insights into health conditions such as anemia, infections, or clotting disorders. (blood cell identification, microscopic analysis)
Tips for Optimal Microscopic Observation

To enhance your microscopy experience, consider these tips:
- Adjust Lighting: Use proper illumination to improve visibility.
- Focus Gradually: Start with lower magnification and gradually increase to higher settings.
- Record Observations: Take notes or capture images for future reference.
- Practice Regularly: The more you observe, the better you’ll become at identifying cell types.
Exploring blood cells under the microscope is not only educational but also a rewarding experience. By following the steps and tips outlined in this guide, you can gain a deeper understanding of the microscopic world within us. Whether for academic, professional, or personal interest, this journey into blood cell microscopy opens doors to endless discoveries. (microscopy tips, blood cell analysis)
What magnification is best for observing blood cells?
+A magnification of 400x to 1000x is ideal for observing blood cells under a microscope.
Can I use fresh blood without staining?
+While fresh blood can be observed, staining enhances cell visibility and differentiation.
How do I differentiate between RBCs and WBCs?
+RBCs are smaller, biconcave, and lack a nucleus, while WBCs are larger, have a nucleus, and appear blue/purple under stain.



