Bohr-Rutherford Diagram for Potassium: Simplified Guide

Understanding the Bohr-Rutherford diagram for potassium is essential for anyone studying chemistry or atomic structure. This simplified guide will walk you through the basics, ensuring you grasp the concept effortlessly. Whether you’re a student, educator, or just curious about atomic models, this post is tailored for you.
Potassium, with its atomic number 19, is a fascinating element to explore. Its Bohr-Rutherford diagram visually represents the arrangement of electrons in its energy levels, making it easier to understand its chemical behavior. Let’s dive in!
What is a Bohr-Rutherford Diagram?
A Bohr-Rutherford diagram is a visual model of an atom, showing the nucleus and the arrangement of electrons in energy levels or shells. It combines Niels Bohr’s theory of quantized energy levels with Ernest Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus. For potassium, this diagram helps illustrate how its 19 electrons are distributed.
📌 Note: The Bohr-Rutherford model is a simplified representation and does not account for modern quantum mechanics concepts like orbitals.
How to Draw the Bohr-Rutherford Diagram for Potassium

Drawing the diagram for potassium involves a few straightforward steps:
- Identify the Atomic Number: Potassium has an atomic number of 19, meaning it has 19 protons and 19 electrons.
- Locate the Nucleus: Place the nucleus at the center, containing 19 protons and 20 neutrons (for the most common isotope, potassium-39).
- Arrange Electrons in Shells: Use the electron configuration 2-8-8-1 to place electrons in the first four shells.
| Shell | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|
| First Shell (K) | 2 |
| Second Shell (L) | 8 |
| Third Shell (M) | 8 |
| Fourth Shell (N) | 1 |

Key Features of Potassium’s Diagram
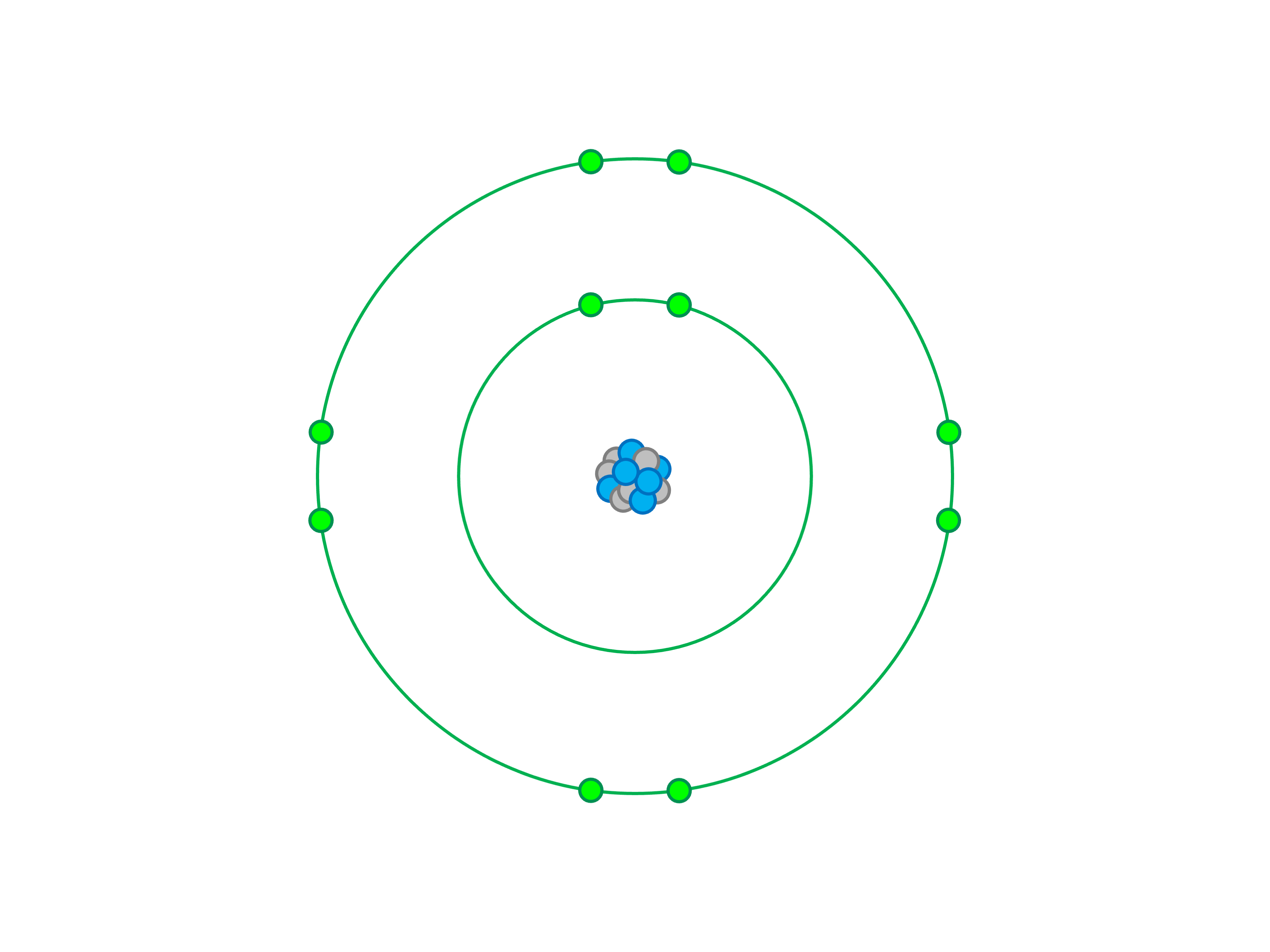
- Valence Electron: Potassium has one electron in its outermost shell, making it highly reactive.
- Electron Configuration: The configuration 2-8-8-1 highlights its stability and reactivity.
- Atomic Structure: The nucleus contains 19 protons and 20 neutrons, with electrons orbiting in defined shells.
✨ Note: The single valence electron in the fourth shell is crucial for potassium’s chemical properties.
Why is Potassium’s Diagram Important?

Understanding potassium’s Bohr-Rutherford diagram is vital for:
- Predicting its chemical reactions.
- Explaining its role in biological processes, such as nerve function.
- Studying its applications in industries like agriculture and medicine.
Checklist for Drawing Potassium’s Diagram

- [ ] Identify the atomic number (19).
- [ ] Place the nucleus with 19 protons and 20 neutrons.
- [ ] Arrange electrons in shells: 2, 8, 8, 1.
- [ ] Highlight the valence electron in the fourth shell.
Wrapping Up
The Bohr-Rutherford diagram for potassium is a powerful tool for visualizing its atomic structure. By following this guide, you can easily draw and understand the diagram, enhancing your knowledge of chemistry. Whether for academic purposes or personal curiosity, mastering this concept opens doors to deeper exploration of atomic theory.
What is the electron configuration of potassium?
+Potassium's electron configuration is 2-8-8-1, with one electron in the outermost shell.
Why does potassium have only one valence electron?
+Potassium has one valence electron because its electron configuration ends with a single electron in the fourth shell.
How does the Bohr-Rutherford diagram help in chemistry?
+It helps predict chemical behavior by showing electron arrangement and valence electrons.
Related Keywords: Bohr-Rutherford diagram, potassium atomic structure, electron configuration, valence electrons, atomic model.


