Mastering the Disk Diffusion Method: A Quick Guide

The disk diffusion method is a cornerstone technique in microbiology, widely used to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria. Whether you're a student, researcher, or healthcare professional, mastering this method is essential for accurate results. This quick guide walks you through the process step-by-step, ensuring you understand the principles and practicalities of the disk diffusion method. From preparing your materials to interpreting results, we’ve got you covered. Let’s dive in! (antimicrobial testing, disk diffusion technique, microbiology lab)
Understanding the Disk Diffusion Method

The disk diffusion method, also known as the Kirby-Bauer test, is a simple yet effective way to assess how susceptible bacteria are to different antibiotics. It involves placing antibiotic-impregnated disks on an agar plate inoculated with bacteria. The zone of inhibition around each disk indicates the antibiotic’s effectiveness. This method is widely used in clinical and research settings for its reliability and ease of use. (antibiotic susceptibility testing, Kirby-Bauer test, zone of inhibition)
Key Components of the Disk Diffusion Method
- Agar Plate: A solid medium where bacteria grow.
- Antibiotic Disks: Filter paper disks infused with specific antibiotics.
- Bacterial Inoculum: A standardized suspension of bacteria.
- Incubator: Maintains optimal conditions for bacterial growth.
💡 Note: Ensure all materials are sterile to avoid contamination.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing the Disk Diffusion Method
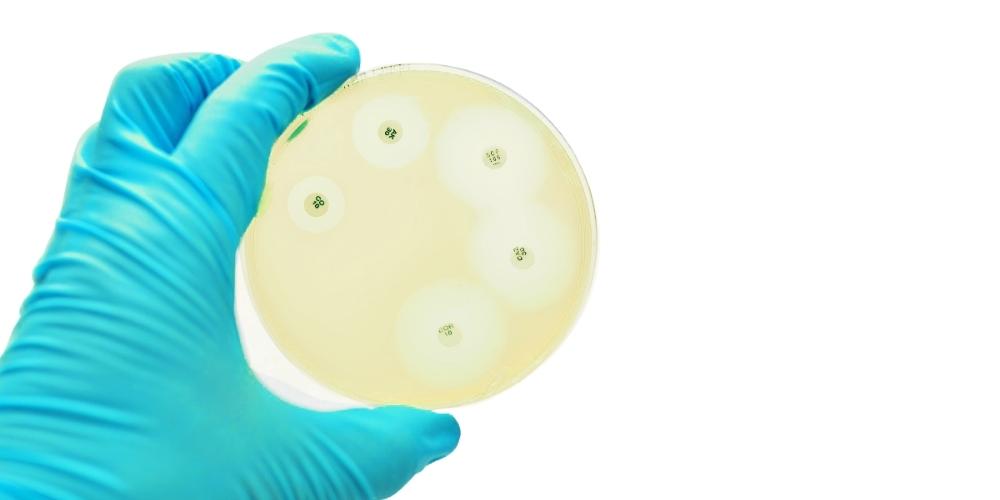
Follow these steps to perform the disk diffusion method accurately:
Step 1: Prepare the Bacterial Inoculum
- Suspend the bacteria in saline to match the 0.5 McFarland standard.
- Spread the inoculum evenly on the agar plate using a sterile swab.
✨ Note: A uniform lawn of bacteria is crucial for accurate results.
Step 2: Place the Antibiotic Disks
- Using sterile forceps, place the antibiotic disks on the agar surface.
- Ensure disks are evenly spaced to prevent overlapping zones.
Step 3: Incubate the Plate
- Incubate the plate at 37°C for 18–24 hours.
- Avoid disturbing the plate during incubation.
Step 4: Measure the Zones of Inhibition
- Use a ruler to measure the diameter of each zone in millimeters.
- Compare measurements to standard guidelines for interpretation.
Interpreting Results: What Do the Zones Mean?
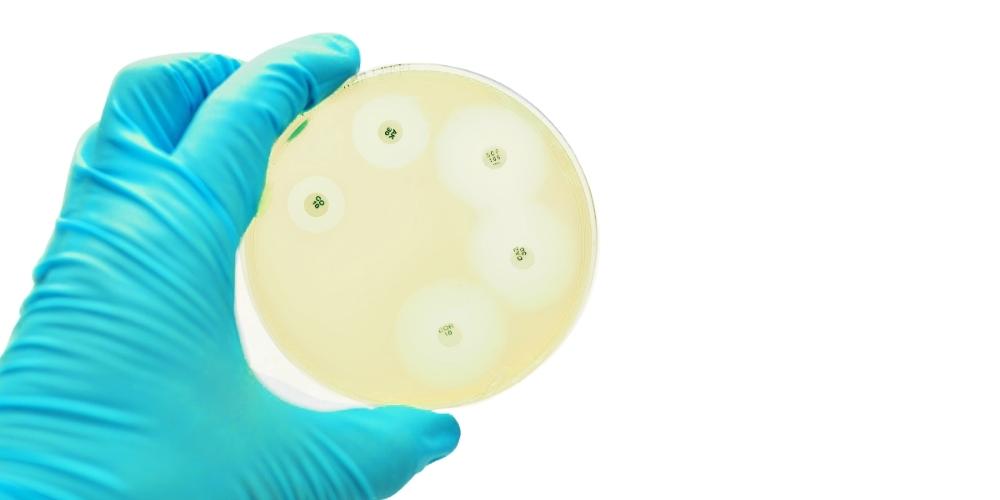
The size of the zone of inhibition indicates the antibiotic’s effectiveness:
| Zone Size | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Large Zone | Sensitive (bacteria are susceptible to the antibiotic) |
| Small Zone | Resistant (bacteria are not affected by the antibiotic) |
| No Zone | Highly Resistant |

Quick Checklist for Disk Diffusion Success
- ✅ Use fresh agar plates and sterile materials.
- ✅ Standardize the bacterial inoculum.
- ✅ Place disks evenly and avoid overcrowding.
- ✅ Incubate at the correct temperature and duration.
- ✅ Measure zones accurately for reliable results.
Mastering the disk diffusion method is a valuable skill in microbiology, enabling accurate assessment of antibiotic susceptibility. By following this guide, you’ll ensure precise and reliable results in your experiments. Remember, attention to detail and adherence to protocols are key to success. Happy testing! (microbiology techniques, antibiotic resistance, lab protocols)
What is the disk diffusion method used for?
+
The disk diffusion method is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics by measuring the zone of inhibition around antibiotic-impregnated disks.
How do I standardize the bacterial inoculum?
+
Standardize the inoculum by suspending the bacteria in saline to match the 0.5 McFarland standard, ensuring consistent bacterial density.
What does a large zone of inhibition indicate?
+
A large zone of inhibition indicates that the bacteria are sensitive to the antibiotic, meaning the antibiotic is effective against them.



