Does Plantae Contain Chitin? Surprising Facts Revealed.

Have you ever wondered if plants contain chitin, a substance commonly associated with the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans? This question piques the curiosity of botanists, gardeners, and biology enthusiasts alike. While chitin is a well-known component in the animal kingdom, its presence in the plant kingdom, or Plantae, is a topic of much debate and scientific exploration. In this post, we’ll delve into the surprising facts about chitin and its relationship with plants, shedding light on this fascinating aspect of botany. (plant biology, chitin in plants, Plantae composition)
What is Chitin and Why Does it Matter?

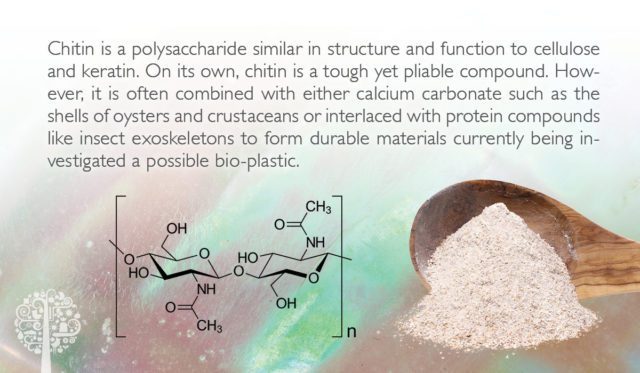
Chitin is a complex carbohydrate and a key component of fungal cell walls, arthropod exoskeletons, and certain animal tissues. It provides structural support and protection, making it essential for the survival of many organisms. But what about plants? Do they utilize this remarkable substance, or is it exclusive to other life forms? Understanding chitin’s role in different organisms can help us appreciate its potential significance in Plantae. (chitin definition, chitin function, chitin in fungi)
The Role of Chitin in Fungi vs. Plants

Fungi, which were once classified under Plantae, are now recognized as a separate kingdom. They rely heavily on chitin for their cell walls, which distinguishes them from plants. Plants, on the other hand, use cellulose as their primary structural component. However, recent studies have uncovered intriguing interactions between plants and chitin-containing organisms, raising questions about whether plants can produce or utilize chitin in any capacity. (fungi and chitin, plant cell walls, cellulose vs chitin)
Surprising Discoveries: Chitin in Plant Interactions

While plants do not naturally produce chitin, they have evolved mechanisms to recognize and respond to it. For instance, chitin triggers immune responses in plants, acting as a signal for potential fungal or insect invasions. This interaction highlights the intricate relationship between plants and chitin-containing organisms. Additionally, some plants benefit from symbiotic relationships with chitin-degrading bacteria, which help them access nutrients in the soil. (plant immunity, chitin recognition, symbiotic relationships)
🌱 Note: Plants do not synthesize chitin but can detect and respond to it through specialized receptors.
Commercial Applications: Chitin in Agriculture

For those with commercial interests, chitin’s role in agriculture is particularly noteworthy. Chitin-based products are increasingly used as organic pesticides, soil amendments, and plant growth promoters. These applications leverage chitin’s ability to enhance plant immunity and improve soil health, offering sustainable solutions for modern farming practices. (chitin in agriculture, organic pesticides, soil health)
| Application | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pesticides | Reduces pest damage naturally |
| Soil Amendments | Improves soil structure and nutrient retention |
| Growth Promoters | Enhances plant vigor and yield |
Key Takeaways: Chitin and Plantae

- Plants do not contain chitin but can recognize and respond to it.
- Chitin plays a crucial role in plant immunity and interactions with other organisms.
- Commercial applications of chitin benefit agriculture through sustainable practices.
In summary, while Plantae does not inherently contain chitin, its interaction with this substance is both fascinating and functionally significant. From immune responses to agricultural innovations, chitin’s role in the plant world is far from insignificant. Whether you’re a botany enthusiast or a farmer, understanding this relationship opens up new avenues for exploration and application. (plant immunity, sustainable agriculture, chitin applications)
Do plants produce chitin?
+No, plants do not produce chitin. They primarily use cellulose for structural support.
How do plants interact with chitin?
+Plants recognize chitin as a signal for potential threats, triggering immune responses to protect against pathogens.
What are the commercial uses of chitin in agriculture?
+Chitin is used in organic pesticides, soil amendments, and plant growth promoters to enhance crop health and yield.



