Uncover Copper's Unique Electronic Configuration Secrets
Copper, a versatile metal with exceptional conductivity, owes its unique properties to its electronic configuration. Understanding this configuration is crucial for both scientific exploration and practical applications. In this post, we’ll delve into the secrets of copper’s electronic structure, its significance in various industries, and how it influences its behavior. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional, this guide will provide valuable insights into copper’s electronic configuration, copper properties, and its real-world applications.
Understanding Copper's Electronic Configuration

The Basics of Copper’s Atomic Structure
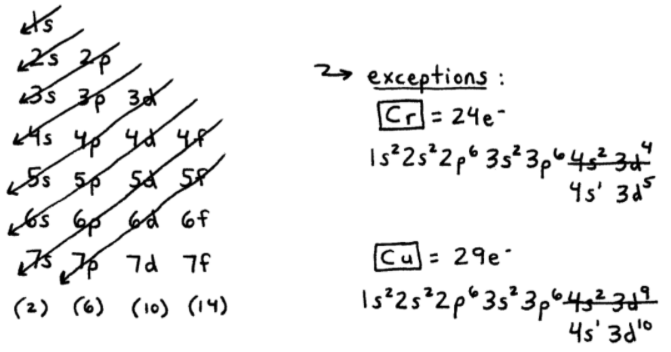
Copper, with an atomic number of 29, has an electronic configuration of [Ar] 3d10 4s1. This arrangement explains its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. The single electron in the 4s orbital is loosely bound, allowing it to move freely and conduct electricity efficiently. This unique setup also contributes to copper’s malleability and ductility, making it ideal for wiring and electronics. (copper atomic structure, copper electron configuration)
Why Copper’s Configuration Matters
Copper’s electronic configuration is the foundation of its chemical behavior and physical properties. The filled 3d orbital provides stability, while the 4s electron enables interactions with other elements. This balance makes copper a key player in industries like electrical engineering, construction, and renewable energy. Understanding this configuration helps in optimizing its use in alloys, such as brass and bronze, and in developing new materials.
Practical Applications of Copper's Electronic Properties

Copper in Electrical Systems
Copper’s high conductivity is unmatched, making it the preferred choice for electrical wiring, motors, and transformers. Its ability to efficiently transmit electricity with minimal energy loss ensures reliability in power grids and electronic devices. Additionally, copper’s resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of electrical systems. (copper conductivity, electrical wiring)
Copper in Renewable Energy
As the world shifts toward sustainable energy, copper plays a vital role in technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Its electronic configuration ensures optimal performance in these systems, contributing to higher energy efficiency. Copper’s recyclability further aligns with green energy goals, reducing environmental impact. (renewable energy, copper sustainability)
💡 Note: Copper’s unique electronic configuration not only enhances its conductivity but also makes it an eco-friendly choice for modern technologies.
Key Takeaways: Copper’s Electronic Configuration
- Copper’s configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s1, enabling high conductivity.
- Its properties make it essential for electrical and renewable energy applications.
- Understanding its structure aids in material science and engineering advancements.
Copper’s electronic configuration is the cornerstone of its versatility and utility across industries. From powering homes to driving renewable energy solutions, its unique structure ensures efficiency and sustainability. By grasping these secrets, we can harness copper’s full potential for future innovations. (copper applications, material science)
What is copper’s electronic configuration?
+Copper’s electronic configuration is [Ar] 3d10 4s1, with a single electron in the 4s orbital.
Why is copper preferred for electrical wiring?
+Copper’s high conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability make it ideal for electrical applications.
How does copper contribute to renewable energy?
+Copper is used in solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems due to its efficiency and recyclability.
Related Terms:
- Copper
- cobalt electron configuration
- tin electron configuration
- carbon electron configuration
- lead electron configuration
- mercury electron configuration



