Exponential vs. Logistic Growth: Key Differences Explained

Understanding the dynamics of growth is crucial in various fields, from biology and economics to technology and environmental science. Two fundamental concepts often discussed are exponential growth and logistic growth. While both describe how populations, resources, or systems increase over time, they differ significantly in their mechanisms and outcomes. This blog post delves into the key differences between exponential and logistic growth, helping you grasp their implications in real-world scenarios.
What is Exponential Growth?
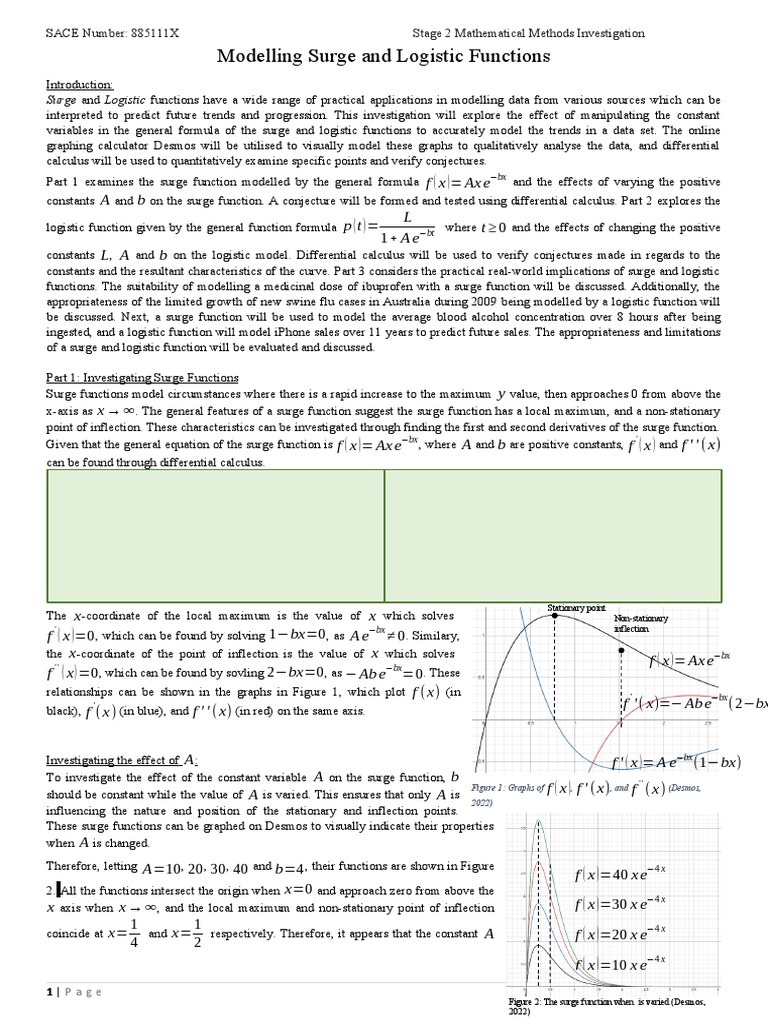
Exponential growth occurs when a quantity increases at a rate proportional to its current value. This means the larger the population or resource, the faster it grows. Mathematically, it follows the formula:
N(t) = N₀ × e^(rt)
Where:
- N(t) = Population at time t
- N₀ = Initial population
- r = Growth rate
- e = Base of the natural logarithm
Key Characteristics of Exponential Growth
- Unlimited Resources: Assumes no constraints on growth factors like food, space, or energy.
- Rapid Increase: Growth accelerates over time, leading to a J-shaped curve.
- Real-World Examples: Early stages of bacterial growth, viral spread, or unchecked technological advancements.
📌 Note: Exponential growth is unsustainable in the long term due to finite resources.
What is Logistic Growth?

Logistic growth accounts for limiting factors that eventually slow down the growth rate. It models real-world scenarios more accurately, where resources are finite. The formula is:
N(t) = K / (1 + (K - N₀) / N₀ × e^(-rt))
Where:
- K = Carrying capacity (maximum population the environment can sustain).
Key Characteristics of Logistic Growth
- Carrying Capacity: Growth slows as the population approaches the environmental limit.
- S-Shaped Curve: Initial exponential growth levels off over time.
- Real-World Examples: Human population growth, predator-prey dynamics, or resource consumption in ecosystems.
| Aspect | Exponential Growth | Logistic Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Assumption | Unlimited | Limited |
| Growth Curve | J-shaped | S-shaped |
| Sustainability | Unsustainable | Sustainable |

When to Use Exponential vs. Logistic Growth

Choosing between these models depends on the context:
- Use exponential growth for short-term predictions or scenarios with abundant resources.
- Opt for logistic growth when long-term sustainability or environmental limits are factors.
Practical Applications

- Business: Exponential growth models early-stage startups, while logistic growth applies to mature markets.
- Ecology: Logistic growth explains population dynamics in ecosystems.
- Technology: Exponential growth describes advancements like Moore’s Law.
Checklist for Choosing the Right Model

- Identify whether resources are limited or unlimited.
- Determine the timeframe of your analysis.
- Consider the carrying capacity of the environment or system.
Understanding exponential vs. logistic growth is essential for making informed decisions in various fields. While exponential growth highlights rapid, unchecked expansion, logistic growth provides a realistic view of sustainability. By recognizing the differences, you can apply these models effectively to predict outcomes and plan strategies.
What is the main difference between exponential and logistic growth?
+Exponential growth assumes unlimited resources and accelerates over time, while logistic growth accounts for limited resources and levels off as it approaches the carrying capacity.
Can exponential growth be sustained indefinitely?
+No, exponential growth is unsustainable in the long term due to finite resources and environmental constraints.
What is the carrying capacity in logistic growth?
+The carrying capacity is the maximum population size that an environment can sustain with available resources.
growth models,population dynamics,resource management,sustainability,mathematical modeling,ecology,economics,technology advancements,J-curve,S-curve.



