Unraveling Forest Food Webs: Nature's Complex Connections Explained

Forests are more than just collections of trees; they are intricate ecosystems where every organism plays a vital role. Forest food webs illustrate the complex connections between plants, animals, and microorganisms, showcasing how energy and nutrients flow through these environments. Understanding these relationships is crucial for conservation efforts, sustainable practices, and appreciating the delicate balance of nature. In this post, we’ll explore the fascinating dynamics of forest food webs, their importance, and how they sustain life on Earth.
What Are Forest Food Webs?

A forest food web is a network of interconnected food chains within a forest ecosystem. Unlike a linear food chain, a food web accounts for multiple interactions, showing how energy transfers between producers (plants), consumers (animals), and decomposers (fungi, bacteria). These webs highlight the interdependence of species and the resilience of forests.
🌿 Note: Forest food webs are dynamic and can change based on seasonal shifts, climate, and human activities.
Key Components of Forest Food Webs

To understand forest food webs, let’s break down their essential components:
- Producers (Plants): Trees, shrubs, and understory plants convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food web.
- Consumers (Animals): These include herbivores (e.g., deer), carnivores (e.g., wolves), and omnivores (e.g., bears) that rely on other organisms for energy.
- Decomposers (Microorganisms): Fungi, bacteria, and insects break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil.
Each component is critical for maintaining the health and stability of the forest ecosystem, (forest ecosystem, ecosystem balance, biodiversity).
Why Are Forest Food Webs Important?
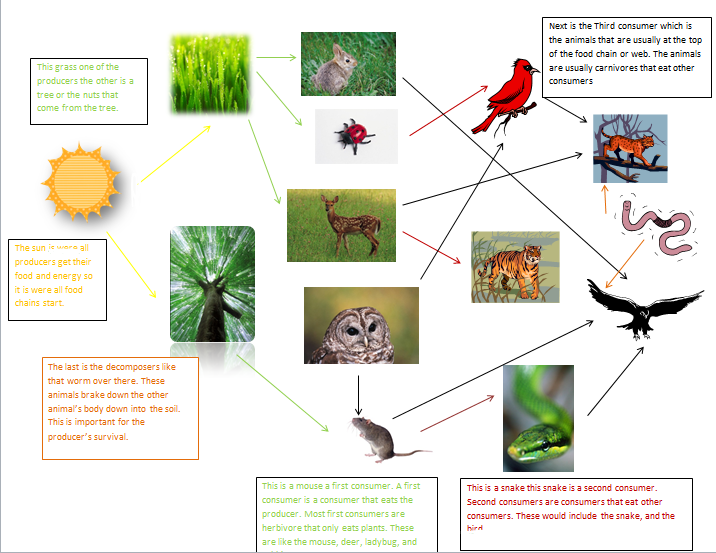
Forest food webs are essential for several reasons:
- Biodiversity Support: They sustain a wide variety of species, promoting genetic diversity and ecosystem resilience.
- Climate Regulation: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and mitigating climate change.
- Resource Cycling: Decomposers ensure nutrients are recycled, maintaining soil fertility and plant growth.
Disrupting these webs can lead to cascading effects, such as species extinction and ecosystem collapse, (biodiversity conservation, climate change, ecosystem services).
Threats to Forest Food Webs
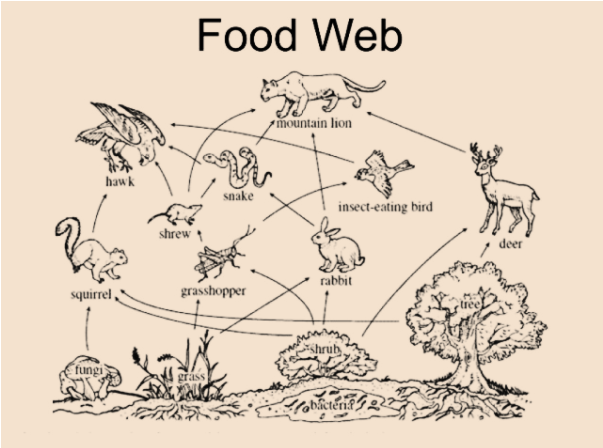
Despite their importance, forest food webs face numerous threats:
| Threat | Impact |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Removes habitats and disrupts energy flow. |
| Pollution | Contaminates soil and water, harming organisms. |
| Climate Change | Alters temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting species survival. |
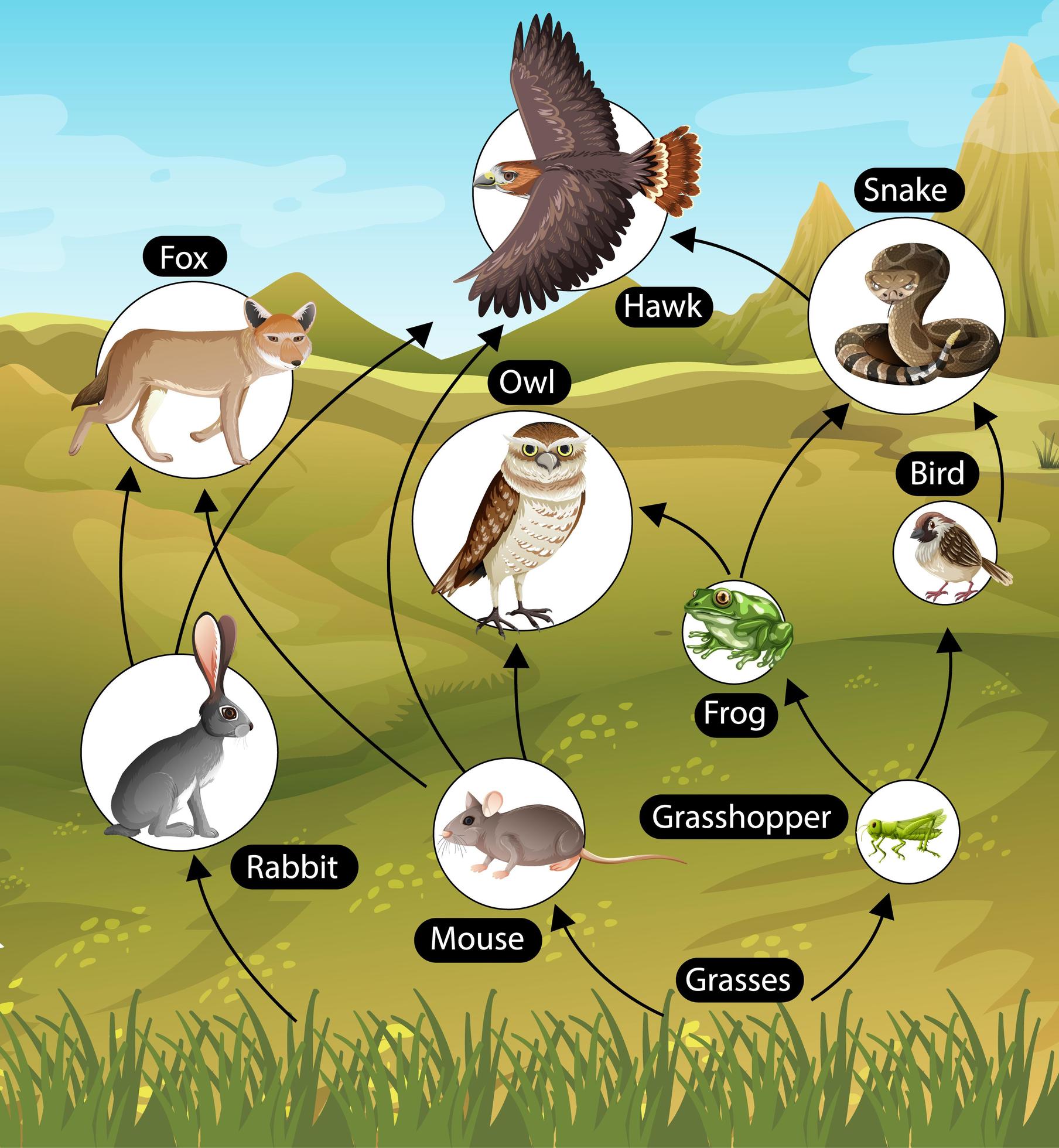
Addressing these threats requires global cooperation and sustainable practices, (deforestation, pollution, climate change mitigation).
How Can We Protect Forest Food Webs?
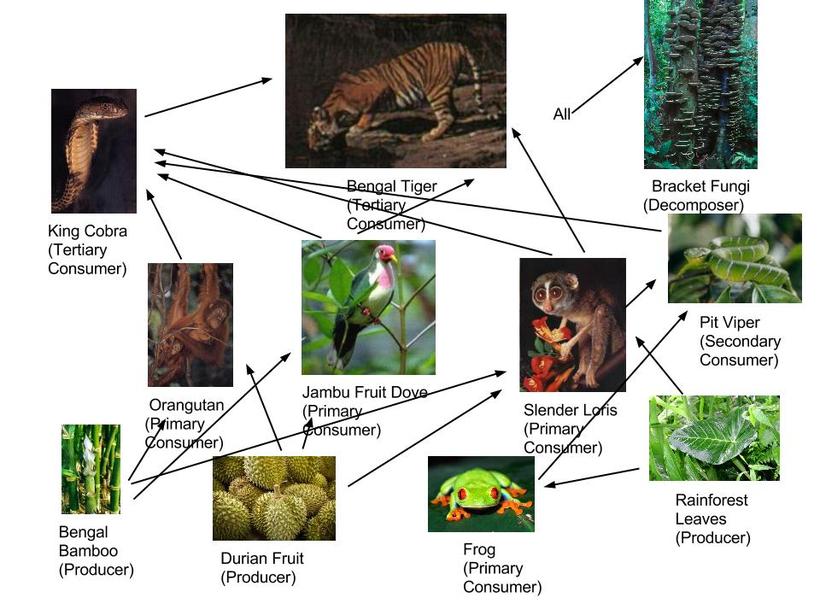
Preserving forest food webs involves both individual and collective actions:
- Reforestation: Planting trees restores habitats and strengthens ecosystems.
- Sustainable Practices: Reduce waste, use eco-friendly products, and support conservation initiatives.
- Education: Raise awareness about the importance of forests and their intricate webs.
By taking these steps, we can ensure the longevity of forest ecosystems, (reforestation, sustainable living, environmental education).
Forest food webs are a testament to nature’s complexity and interconnectedness. By understanding and protecting these systems, we contribute to the health of our planet and future generations. Whether through small daily actions or large-scale conservation efforts, every step counts in preserving these vital ecosystems.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
+
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms showing who eats whom, while a food web is a network of interconnected food chains, illustrating multiple interactions within an ecosystem.
How do decomposers contribute to forest food webs?
+
Decomposers break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil, which supports plant growth and sustains the entire food web.
What are some simple ways to support forest conservation?
+
You can support forest conservation by planting trees, reducing paper usage, supporting eco-friendly products, and participating in local conservation initiatives.


