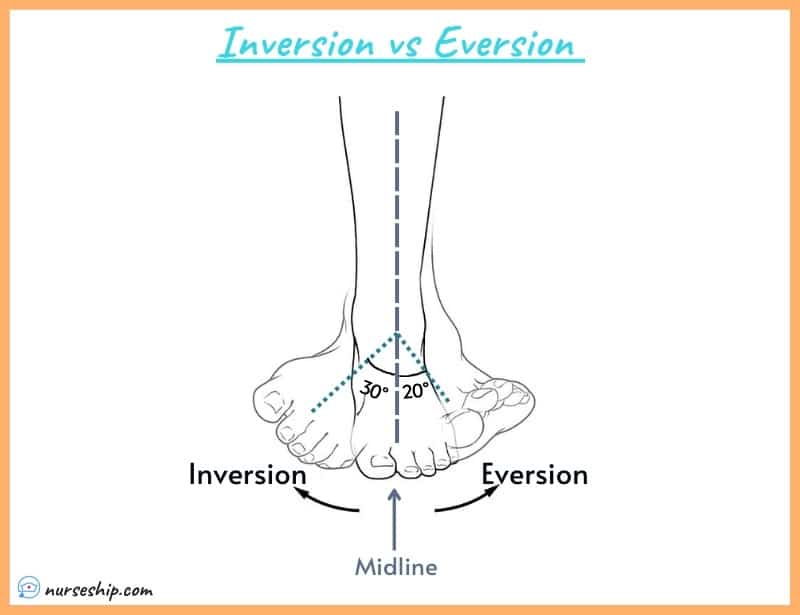
Inversion vs Eversion: Understanding Foot Movements Simplified

Understanding foot movements is essential for anyone dealing with foot health, whether you’re an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or someone experiencing foot discomfort. Inversion and eversion are two fundamental movements of the foot that play a crucial role in stability, mobility, and overall foot function. Let’s break down these concepts in simple terms and explore their significance.
What is Inversion of the Foot?

Inversion refers to the movement of the sole of the foot toward the midline of the body. Imagine tilting your foot inward so that the arch faces upward. This motion is vital for balance and shock absorption during activities like walking or running.
Key Muscles Involved in Inversion
- Tibialis Posterior: Primary muscle responsible for inversion.
- Tibialis Anterior: Assists in stabilizing the foot during inversion.
📌 Note: Weakness in these muscles can lead to issues like flat feet or ankle instability.
What is Eversion of the Foot?

Eversion is the opposite of inversion, where the sole of the foot moves away from the midline of the body. Picture tilting your foot outward so that the arch faces downward. This movement is less common but still important for certain activities and foot mechanics.
Key Muscles Involved in Eversion
- Peroneus Longus and Brevis: Primary muscles responsible for eversion.
- Extensor Digitorum Longus: Assists in the movement.
📌 Note: Overuse or injury to these muscles can result in conditions like peroneal tendonitis.
Inversion vs Eversion: Key Differences

| Aspect | Inversion | Eversion |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | Sole moves inward (arch up) | Sole moves outward (arch down) |
| Primary Muscles | Tibialis Posterior, Tibialis Anterior | Peroneus Longus, Peroneus Brevis |
| Common Issues | Flat feet, ankle sprains | Peroneal tendonitis, ankle instability |

Why Understanding These Movements Matters

Knowing the difference between inversion and eversion is crucial for:
- Injury Prevention: Proper foot mechanics reduce the risk of sprains and strains.
- Rehabilitation: Targeted exercises can strengthen weak muscles and improve mobility.
- Performance Enhancement: Athletes can optimize their movements for better stability and efficiency.
Practical Tips for Healthy Foot Movements
- Stretch Regularly: Incorporate calf and foot stretches to maintain flexibility.
- Strengthen Muscles: Perform exercises like calf raises and resistance band workouts.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Choose shoes that support your foot’s natural arch and movement.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or difficulty moving your foot, consult a podiatrist or physical therapist. Early intervention can prevent long-term issues.
What causes excessive foot inversion?
+Excessive foot inversion is often caused by weak tibialis posterior muscles, flat feet, or improper footwear.
How can I strengthen my foot for better inversion and eversion?
+Exercises like toe curls, ankle alphabet, and resistance band workouts can improve foot strength and stability.
Is eversion as important as inversion?
+While inversion is more common, eversion is still important for certain movements and maintaining balanced foot mechanics.
In summary, understanding inversion and eversion is key to maintaining healthy foot function. By recognizing these movements and their associated muscles, you can take proactive steps to prevent injuries and enhance your overall foot health. Whether you’re an athlete or someone looking to improve daily mobility, this knowledge is invaluable.
(Foot Anatomy, Foot Health Tips, Ankle Stability Exercises)