Understanding Iron II Oxide Formula: A Quick Guide
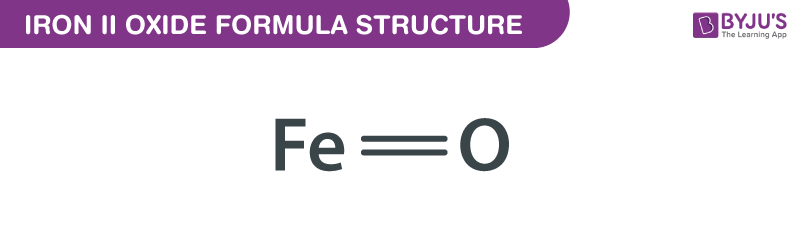
Iron II Oxide, commonly known as ferrous oxide, is a chemical compound with the formula FeO. This inorganic compound plays a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and pigments. Understanding its formula, properties, and applications is essential for both informational and commercial purposes. Whether you're a student, researcher, or industry professional, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of Iron II Oxide, its chemical structure, and its practical uses. (iron ii oxide formula, ferrous oxide, chemical compound)
What is Iron II Oxide?
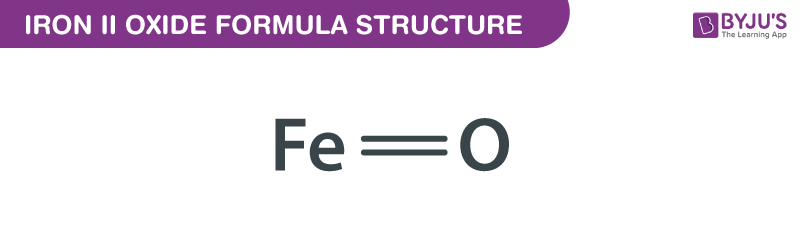
Iron II Oxide (FeO) is a binary compound composed of iron (Fe) and oxygen (O). It exists in a rock salt structure and is primarily known for its black or dark gray color. Unlike its counterpart, Iron III Oxide (Fe₂O₃), which is reddish-brown, FeO has distinct properties that make it valuable in specific applications. Its formula reflects the +2 oxidation state of iron, making it a unique compound in the iron oxide family. (iron ii oxide properties, iron oxide compounds, oxidation state)
Chemical Properties and Formula of Iron II Oxide

The formula FeO represents the simplest form of iron oxide, where one iron atom bonds with one oxygen atom. Here are its key chemical properties:
- Molar Mass: 71.85 g/mol
- Appearance: Black or dark gray crystalline powder
- Solubility: Insoluble in water, slightly soluble in acids
- Melting Point: Approximately 1,377°C (2,511°F)
📌 Note: Iron II Oxide is unstable in air and can oxidize to Iron III Oxide (Fe₂O₃) over time.
Understanding these properties is crucial for applications in industries like ceramics, glassmaking, and metallurgy. (iron ii oxide molar mass, iron oxide solubility, iron oxide melting point)
Applications of Iron II Oxide
Iron II Oxide is widely used across various sectors due to its unique properties. Here are some of its primary applications:
- Pigments: Used in paints, coatings, and inks for its dark color.
- Ceramics: Enhances the color and strength of ceramic materials.
- Metallurgy: Acts as a reducing agent in steel production.
- Glassmaking: Adds color and improves glass properties.
For commercial purposes, sourcing high-quality Iron II Oxide is essential to ensure optimal performance in industrial processes. (iron ii oxide uses, iron oxide pigments, iron oxide in ceramics)
How to Identify and Test Iron II Oxide
Identifying Iron II Oxide requires specific tests to distinguish it from other iron oxides. Here’s a quick checklist:
- Check for black or dark gray color.
- Perform a flame test to observe a green flame, indicative of iron.
- Use chemical tests like the potassium ferricyanide test to confirm Fe²⁺ ions.
📌 Note: Always handle Iron II Oxide with care, as it can oxidize quickly in air.
Accurate identification ensures the compound’s suitability for intended applications. (iron ii oxide identification, iron oxide testing, chemical tests for iron)
Summary Checklist: Key Points About Iron II Oxide

- Formula: FeO (Iron II Oxide)
- Properties: Black color, insoluble in water, high melting point
- Applications: Pigments, ceramics, metallurgy, glassmaking
- Identification: Flame test, chemical tests for Fe²⁺ ions
In summary, Iron II Oxide (FeO) is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications across industries. Its unique chemical properties and formula make it an essential material for both informational research and commercial use. By understanding its characteristics and uses, you can make informed decisions in your projects or business endeavors. (iron ii oxide summary, iron oxide applications, chemical compound overview)
What is the difference between Iron II Oxide and Iron III Oxide?
+
Iron II Oxide (FeO) has a +2 oxidation state and is black, while Iron III Oxide (Fe₂O₃) has a +3 oxidation state and is reddish-brown.
Is Iron II Oxide soluble in water?
+
No, Iron II Oxide is insoluble in water but slightly soluble in acids.
What are the main uses of Iron II Oxide?
+
It is used in pigments, ceramics, metallurgy, and glassmaking due to its color and chemical properties.