Is CO2 Ionic or Covalent? Understanding Its Chemical Bonding

<!DOCTYPE html>
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a molecule that plays a crucial role in our atmosphere, but its chemical nature often sparks curiosity. A common question arises: Is CO2 ionic or covalent? Understanding the type of bonding in CO2 is essential for grasping its properties and behavior in various contexts, from climate science to industrial applications.
What is Ionic Bonding?
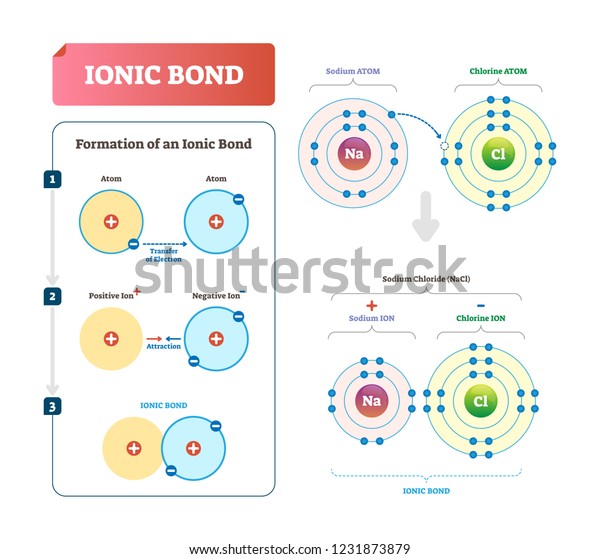
Ionic bonding occurs when electrons are transferred from one atom to another, creating ions with opposite charges that attract each other. This type of bonding is common in compounds like sodium chloride (NaCl). CO2 does not exhibit ionic bonding because its atoms share electrons rather than transferring them.
What is Covalent Bonding?
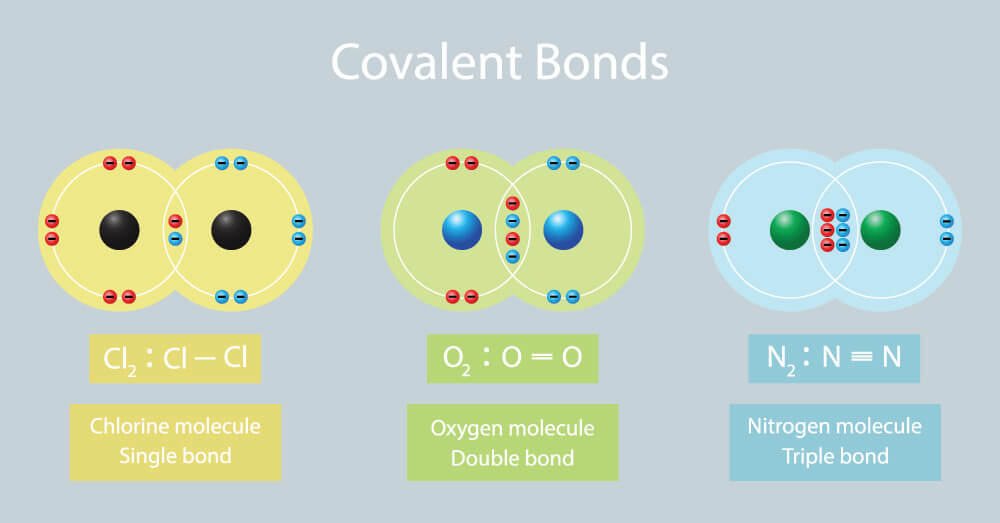
Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration. In CO2, carbon shares electrons with two oxygen atoms, forming double covalent bonds. This sharing results in a stable molecule with a linear structure.
Why CO2 is Covalent, Not Ionic

CO2 is classified as a covalent compound due to the following reasons:
- Electron Sharing: Carbon and oxygen atoms share electrons to complete their outer shells.
- Non-Metal Atoms: Both carbon and oxygen are non-metals, and non-metals typically form covalent bonds.
- Molecular Structure: CO2 exists as discrete molecules, a characteristic of covalent compounds.
| Bond Type | CO2 Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Ionic | Not applicable (no electron transfer) |
| Covalent | Electron sharing, molecular structure |

Key Takeaways: CO2 Bonding

- CO2 is a covalent compound, not ionic.
- It forms double covalent bonds between carbon and oxygen atoms.
- Understanding its bonding helps explain its role in the environment and industrial processes.
📌 Note: CO2’s covalent nature is crucial for its stability and reactivity in chemical reactions, making it a key player in both natural and industrial settings.
In summary, CO2 is a covalent molecule due to the sharing of electrons between carbon and oxygen atoms. This understanding is fundamental for appreciating its role in climate science, chemistry, and various applications. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious, knowing the chemical bonding of CO2 enhances your grasp of its significance in our world.
Is CO2 polar or nonpolar?
+CO2 is nonpolar because its linear structure and symmetrical arrangement of bonds cancel out any dipole moments.
Can CO2 form ionic bonds under any conditions?
+No, CO2 cannot form ionic bonds under normal conditions due to the nature of its atoms and their electron sharing.
Why is understanding CO2 bonding important?
+Understanding CO2 bonding is crucial for studying its role in climate change, chemical reactions, and industrial applications.