Mastering the Lewis Structure for C6H6: Benzene Explained

<!DOCTYPE html>
Understanding the Lewis structure of C6H6 (benzene) is essential for anyone studying organic chemistry or molecular structures. Benzene, a key aromatic hydrocarbon, has a unique arrangement of atoms that can be challenging to visualize. This guide breaks down the process step-by-step, ensuring you grasp the concept effortlessly. Whether you’re a student, educator, or chemistry enthusiast, this post will help you master benzene’s Lewis structure, its resonance forms, and its significance in chemical reactions.
What is the Lewis Structure of C6H6?
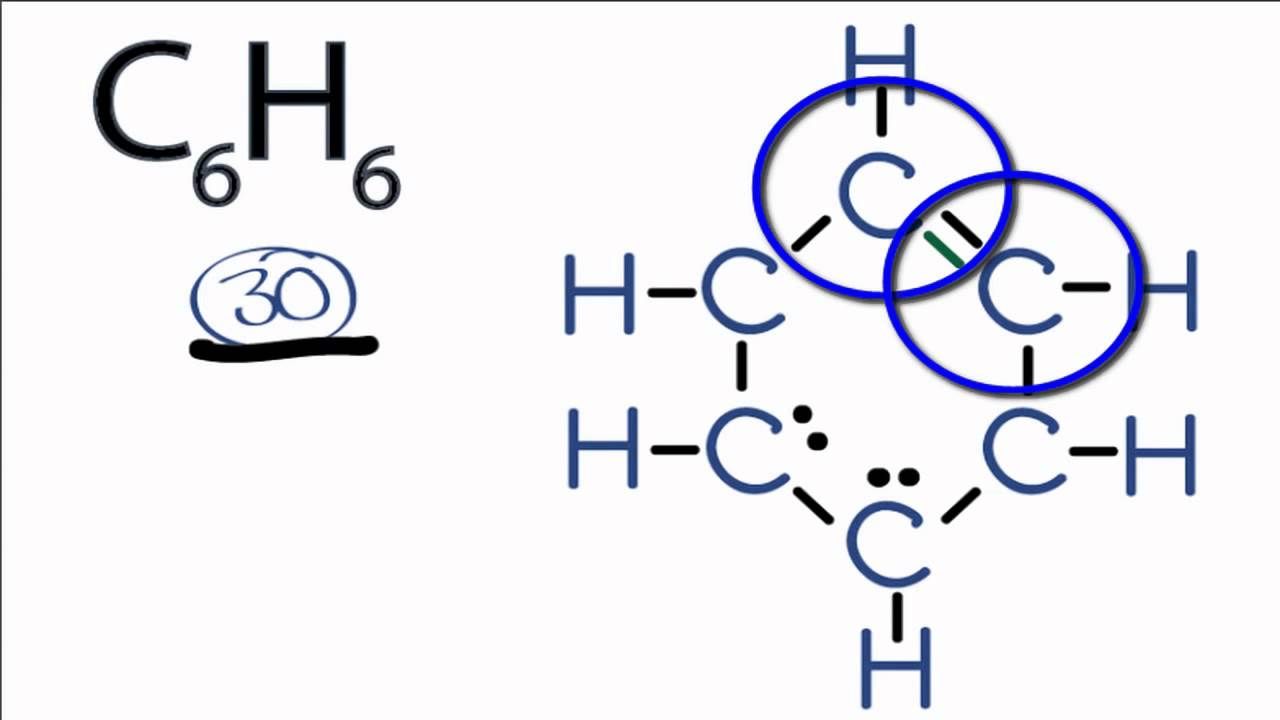
The Lewis structure of benzene (C6H6) represents the arrangement of atoms and electrons in this aromatic compound. It consists of a hexagonal ring of six carbon atoms, each bonded to one hydrogen atom. The unique feature of benzene is its delocalized pi electrons, which are represented by alternating double bonds in its resonance structures. This stability makes benzene a fundamental molecule in organic chemistry.
📌 Note: Benzene’s structure is often depicted with a circle inside the hexagon to represent its delocalized electrons.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing the Lewis Structure of C6H6

Drawing the Lewis dot structure for benzene involves a systematic approach. Follow these steps to ensure accuracy:
- Step 1: Count the total number of valence electrons. Benzene has 6 carbon atoms (4 valence electrons each) and 6 hydrogen atoms (1 valence electron each), totaling 30 valence electrons.
- Step 2: Arrange the atoms in a hexagonal shape. Place the six carbon atoms in a ring and attach one hydrogen atom to each carbon.
- Step 3: Form single bonds between carbon atoms. Connect each carbon atom to its neighbors with single bonds, using 12 electrons.
- Step 4: Add remaining electrons as lone pairs or double bonds. Use the remaining 18 electrons to form alternating double bonds or represent them as a circle inside the hexagon for resonance stability.
Understanding Resonance in Benzene

Benzene’s resonance structures are crucial to its stability. The delocalized pi electrons create a cloud of electron density above and below the ring, making all carbon-carbon bonds equivalent. This phenomenon is known as resonance hybridization, which lowers the overall energy of the molecule.
| Resonance Structure 1 | Resonance Structure 2 |
|---|---|
| Double bonds between C1-C2, C3-C4, C5-C6 | Double bonds between C2-C3, C4-C5, C6-C1 |

Practical Applications of Benzene’s Structure

The Lewis structure of C6H6 is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various fields. Benzene is a precursor in the synthesis of plastics, pharmaceuticals, and dyes. Understanding its structure helps chemists predict its reactivity in substitution and addition reactions.
📌 Note: Benzene’s aromaticity makes it less reactive than typical alkenes, a property leveraged in industrial processes.
Checklist for Mastering Benzene’s Lewis Structure

- Count valence electrons: 30 for C6H6.
- Arrange atoms in a hexagonal ring.
- Form single bonds between carbon atoms.
- Represent delocalized electrons with a circle or alternating double bonds.
- Understand resonance hybridization for stability.
By following this guide, you’ll confidently master the Lewis structure of benzene (C6H6), its resonance forms, and its practical implications. Whether for academic purposes or professional applications, this knowledge is invaluable in the world of chemistry,Lewis structure of C6H6,benzene resonance structures,organic chemistry basics.
Why is benzene’s structure considered aromatic?
+Benzene is aromatic due to its planar, cyclic structure with delocalized pi electrons, following Hückel’s rule (4n+2 electrons in a conjugated system).
How do you count valence electrons for C6H6?
+Carbon has 4 valence electrons, and hydrogen has 1. With 6 carbons and 6 hydrogens, the total is (6*4) + (6*1) = 30 valence electrons.
What is the difference between benzene’s Lewis structure and its resonance forms?
+The Lewis structure shows the basic arrangement of atoms and electrons, while resonance forms depict the delocalized electrons and alternating double bonds.