lewis structure hydrogen
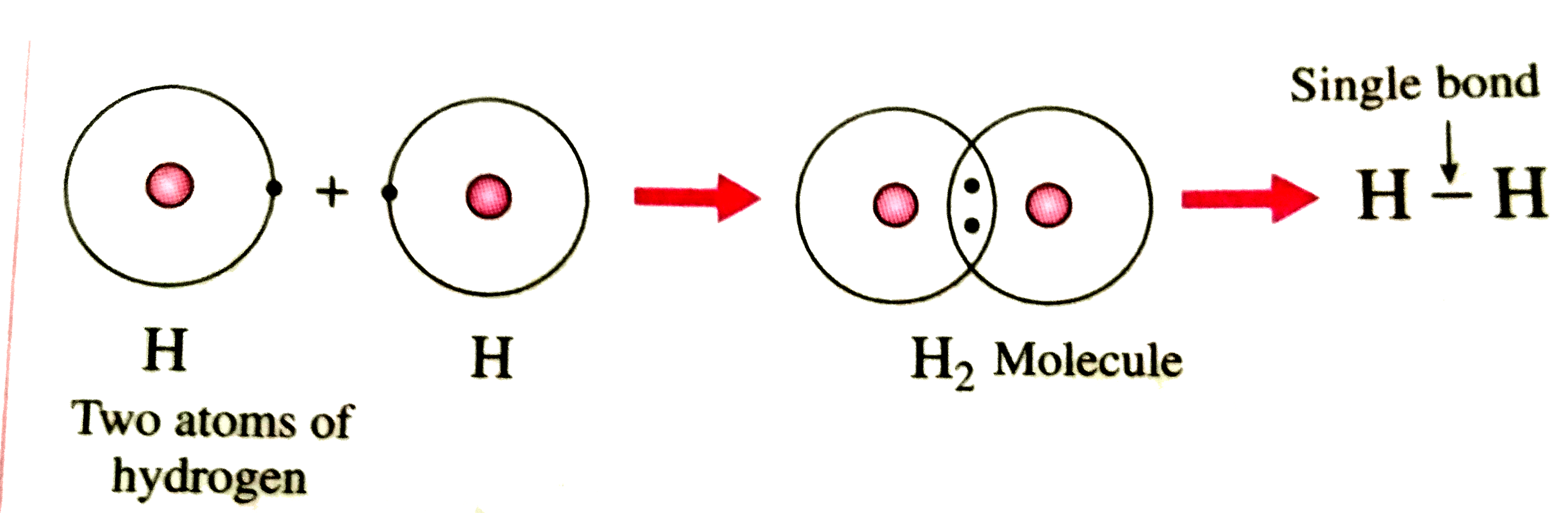
Understanding the Lewis Structure of Hydrogen is essential for anyone studying chemistry or working in fields that require a deep understanding of molecular bonding. The Lewis structure is a visual representation that shows how atoms are connected and where electrons are distributed within a molecule. For hydrogen, the simplest element, its Lewis structure is straightforward yet foundational for grasping more complex molecules.
Hydrogen, with its single electron, forms the basis for understanding covalent bonding. In its Lewis structure, hydrogen is represented with a single electron dot or a bond, reflecting its tendency to share electrons to achieve a stable configuration. This simplicity makes hydrogen an ideal starting point for learning about molecular structures.
What is a Lewis Structure?

A Lewis structure, also known as an electron dot diagram, illustrates the arrangement of atoms and electrons in a molecule. It uses dots to represent valence electrons and lines to depict bonds between atoms. For hydrogen, the Lewis structure is particularly simple due to its single valence electron.
Key Components of a Lewis Structure
- Atoms: Represented by their chemical symbols.
- Valence Electrons: Shown as dots around the atom.
- Bonds: Illustrated as lines connecting atoms.
For hydrogen (H), the Lewis structure consists of the symbol “H” with one dot representing its single valence electron. When hydrogen forms a bond, such as in H₂, the dots are replaced by a line, indicating a shared pair of electrons.
📌 Note: Hydrogen typically forms only one bond due to its single valence electron.
How to Draw the Lewis Structure of Hydrogen

Drawing the Lewis structure of hydrogen is a simple process. Follow these steps:
- Identify the Atom: Hydrogen (H) has one valence electron.
- Place the Electron: Represent the electron as a dot next to the hydrogen symbol.
- Form Bonds: In H₂, replace the dots with a line to show the covalent bond.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify hydrogen (H) with one valence electron. |
| 2 | Place a dot next to H to represent the electron. |
| 3 | For H₂, replace dots with a line to show bonding. |

Example: Lewis Structure of H₂
In H₂, two hydrogen atoms share their electrons to form a covalent bond. The Lewis structure is represented as H-H, with the line indicating the shared electron pair.
📌 Note: H₂ is the most stable form of hydrogen due to the shared electron pair.
Importance of Hydrogen’s Lewis Structure
Understanding the Lewis structure of hydrogen is crucial for several reasons:
- Foundation for Chemistry: It introduces the concept of electron sharing in covalent bonds.
- Building Complex Molecules: Hydrogen is a common element in organic and inorganic compounds.
- Practical Applications: Knowledge of hydrogen bonding is vital in fields like pharmaceuticals and materials science.
Checklist for Drawing Lewis Structures
- Identify the total number of valence electrons.
- Arrange atoms with the least electronegative element in the center.
- Form bonds by pairing electrons.
- Ensure all atoms achieve a stable electron configuration.
What is the Lewis structure of hydrogen?
+The Lewis structure of hydrogen (H) is represented by the symbol "H" with one dot for its single valence electron. In H₂, it is shown as H-H, indicating a covalent bond.
Why is hydrogen’s Lewis structure important?
+Hydrogen’s Lewis structure is foundational for understanding covalent bonding and serves as a basis for learning more complex molecular structures.
How does hydrogen form bonds in its Lewis structure?
+Hydrogen forms bonds by sharing its single valence electron with another atom, typically resulting in a covalent bond, as seen in H₂.
In summary, the Lewis structure of hydrogen is a fundamental concept in chemistry that illustrates the simplicity of hydrogen’s electron configuration and its role in covalent bonding. By mastering this basic structure, you can build a strong foundation for understanding more complex molecules. Whether you’re a student or a professional, this knowledge is invaluable for various scientific and industrial applications.
lewis structure hydrogen, hydrogen lewis dot structure, covalent bonding, molecular structure, chemistry basics



