Understanding the Lewis Structure of PH3: A Quick Guide
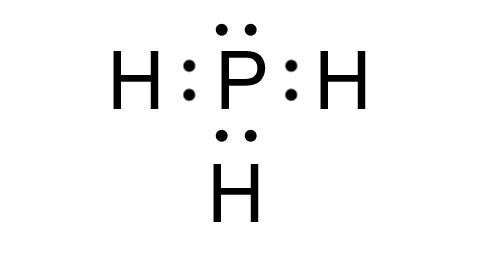
Understanding the Lewis structure of PH3 is essential for anyone studying chemistry, especially in the context of molecular geometry and chemical bonding. PH3, or phosphine, is a simple yet intriguing molecule that plays a significant role in various chemical processes. In this guide, we’ll break down the steps to draw the Lewis structure of PH3, explain its significance, and provide practical tips for mastering this concept.
What is the Lewis Structure of PH3?
The Lewis structure is a visual representation of the arrangement of atoms and electrons in a molecule. For PH3, it helps us understand how phosphorus (P) and hydrogen (H) atoms bond and share electrons. Phosphine consists of one phosphorus atom and three hydrogen atoms, making it a tetraatomic molecule.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing the Lewis Structure of PH3
Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
- Phosphorus (P) has 5 valence electrons.
- Each hydrogen (H) atom has 1 valence electron.
- Total valence electrons = 5 (P) + 3 × 1 (H) = 8 electrons.
- Phosphorus (P) has 5 valence electrons.
Arrange the Atoms
- Place the phosphorus atom in the center, as it is less electronegative than hydrogen.
- Connect the three hydrogen atoms to the phosphorus atom using single bonds.
- Place the phosphorus atom in the center, as it is less electronegative than hydrogen.
Complete the Octet Rule
- Each hydrogen atom already has a full outer shell with 2 electrons (1 from P and 1 from H).
- Phosphorus will have one lone pair of electrons to satisfy its octet.
- Each hydrogen atom already has a full outer shell with 2 electrons (1 from P and 1 from H).
📌 Note: Phosphorus in PH3 has a lone pair, which is crucial for understanding its molecular geometry.
Molecular Geometry of PH3
The Lewis structure of PH3 reveals its trigonal pyramidal geometry. The lone pair on the phosphorus atom repels the bonding pairs, causing the molecule to adopt this shape. This geometry is a key factor in PH3’s chemical properties and reactivity.
| Parameter | PH3 Details |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | PH3 |
| Total Valence Electrons | 8 |
| Molecular Geometry | Trigonal Pyramidal |
| Hybridization | sp3 |
Practical Tips for Mastering Lewis Structures
- Practice Regularly: Draw Lewis structures for other molecules to reinforce your understanding.
- Use Formal Charge: Calculate formal charges to ensure the most stable structure.
- Understand Electronegativity: It determines how atoms share electrons in a bond.
📌 Note: Always double-check the total number of valence electrons to avoid errors.
Why is PH3 Important?

PH3 is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in industries like semiconductors and pharmaceuticals. Understanding its Lewis structure helps chemists predict its behavior in reactions and design new compounds.
To summarize, mastering the Lewis structure of PH3 involves calculating valence electrons, arranging atoms, and applying the octet rule. Its trigonal pyramidal geometry and lone pair are critical to its properties. Practice and attention to detail will make you proficient in drawing Lewis structures for any molecule.
What is the molecular geometry of PH3?
+The molecular geometry of PH3 is trigonal pyramidal due to the lone pair on the phosphorus atom.
How many valence electrons are in PH3?
+PH3 has a total of 8 valence electrons (5 from P and 3 from H atoms).
What is the hybridization of phosphorus in PH3?
+The hybridization of phosphorus in PH3 is sp3.
Lewis structure of PH3, molecular geometry of PH3, PH3 hybridization, valence electrons in PH3, trigonal pyramidal shape



