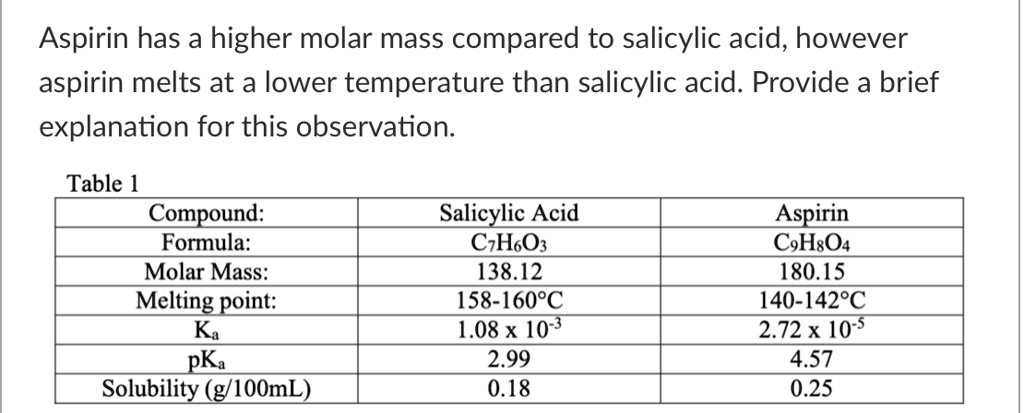
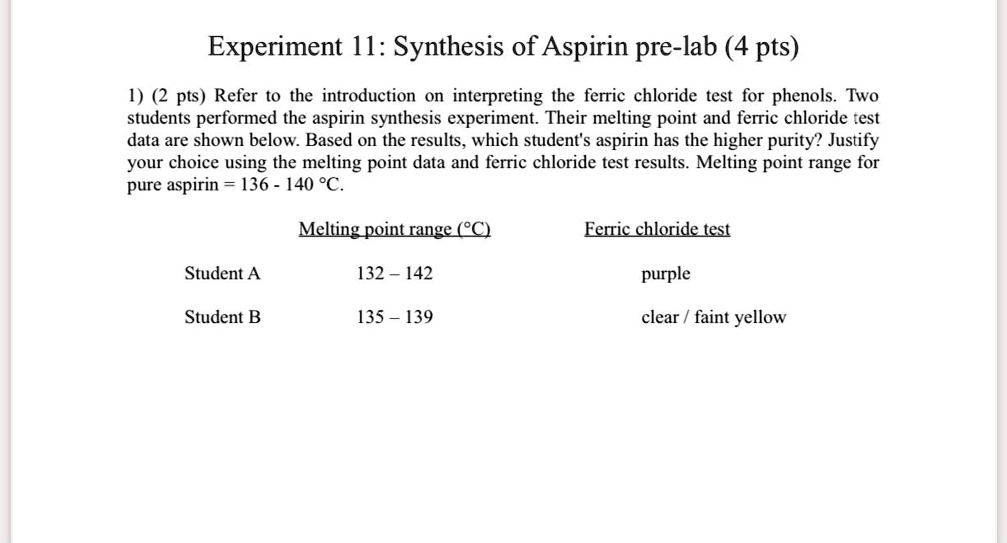
Melting Point of Aspirin: Key Facts & Insights

Understanding the melting point of aspirin is crucial for both scientific research and pharmaceutical applications. Aspirin, chemically known as acetylsalicylic acid, is a widely used medication with a specific melting point that plays a vital role in its manufacturing and quality control. This post explores key facts and insights about the melting point of aspirin, its significance, and practical applications.
What is the Melting Point of Aspirin?

The melting point of aspirin typically ranges between 138°C to 140°C (280°F to 284°F). This narrow range is essential for ensuring the purity and effectiveness of the medication. Deviations from this range may indicate impurities or incorrect formulation, making it a critical parameter in pharmaceutical analysis.
Why is the Melting Point of Aspirin Important?

The melting point of aspirin serves as a key indicator of its quality and consistency. It helps:
- Verify Purity: A precise melting point confirms the absence of contaminants.
- Ensure Efficacy: Proper melting behavior guarantees the drug’s therapeutic effectiveness.
- Standardize Manufacturing: It aids in maintaining uniform production processes.
💡 Note: Accurate measurement of the melting point of aspirin requires calibrated equipment and controlled conditions.
How to Determine the Melting Point of Aspirin
Measuring the melting point of aspirin involves the following steps:
1. Prepare a Sample: Crush a small amount of aspirin into a fine powder.
2. Use a Melting Point Apparatus: Place the sample in a capillary tube and insert it into the device.
3. Heat Gradually: Increase the temperature at a controlled rate (typically 1-2°C per minute).
4. Record Observations: Note the temperature range where the aspirin transitions from solid to liquid.
Factors Affecting the Melting Point of Aspirin
Several factors can influence the melting point of aspirin:
- Impurities: Contaminants can lower the melting point.
- Polymorphism: Different crystal structures may exhibit varying melting points.
- Moisture Content: Water presence can alter the observed melting range.
Practical Applications of Aspirin’s Melting Point

Understanding the melting point of aspirin is beneficial in:
- Pharmaceutical Testing: Ensuring drug compliance with regulatory standards.
- Research & Development: Studying aspirin’s physical properties for new formulations.
- Quality Control: Detecting substandard or counterfeit products.
Checklist for Melting Point Analysis
When working with the melting point of aspirin, keep these points in mind:
- Use a calibrated melting point apparatus.
- Ensure the sample is dry and free from impurities.
- Record temperature accurately within the specified range.
- Compare results with standard reference values.
| Parameter | Ideal Condition |
|---|---|
| Melting Point Range | 138°C to 140°C |
| Heating Rate | 1-2°C per minute |
| Sample Preparation | Fine powder in capillary tube |

The melting point of aspirin is a fundamental property that ensures its reliability and safety. By mastering its measurement and understanding its implications, professionals can uphold the highest standards in pharmaceutical production and research.
What is the melting point of aspirin?
+The melting point of aspirin ranges between 138°C to 140°C (280°F to 284°F).
Why is the melting point of aspirin important?
+It ensures purity, efficacy, and standardization in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
How is the melting point of aspirin measured?
+Using a melting point apparatus with a controlled heating rate and a prepared aspirin sample.
melting point of aspirin, pharmaceutical analysis, aspirin purity, quality control, pharmaceutical manufacturing



