Is NaCl Polar or Nonpolar? The Truth Revealed.
When it comes to understanding the nature of chemical compounds, the question of whether a substance is polar or nonpolar is crucial. One such compound that often sparks curiosity is NaCl, commonly known as table salt. This blog post delves into the truth about NaCl's polarity, exploring its molecular structure, properties, and implications. Whether you're a student, a chemist, or simply curious, this guide will provide clarity on the topic of is NaCl polar or nonpolar.
Understanding Polarity in Chemical Compounds

What Does Polarity Mean?
Polarity refers to the separation of electric charge in a molecule, leading to a positive and negative end. Polar molecules have an uneven distribution of charge, while nonpolar molecules have an even distribution. This distinction is vital in chemistry, affecting properties like solubility and reactivity. Understanding whether NaCl is polar or nonpolar requires examining its molecular structure and bonding.
Key Factors Determining Polarity
To determine if a compound like NaCl is polar or nonpolar, consider the following factors:
- Electronegativity Difference: The difference in electronegativity between atoms in a bond.
- Molecular Geometry: The shape of the molecule, which influences charge distribution.
- Type of Bonding: Ionic or covalent bonding plays a significant role in polarity.
The Molecular Structure of NaCl
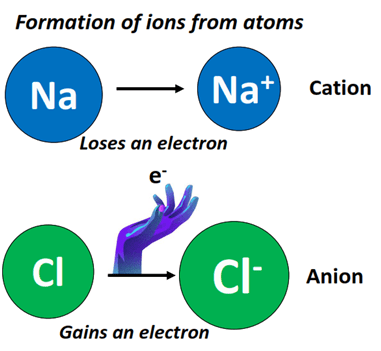
Ionic Bonding in NaCl
NaCl consists of sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) atoms bonded through an ionic bond. In this bond, sodium donates an electron to chlorine, creating Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions. This transfer of electrons results in a strong electrostatic attraction between the ions, characteristic of ionic compounds.
Is NaCl Polar or Nonpolar?
Despite the ionic nature of NaCl, the question of its polarity is often misunderstood. NaCl is considered nonpolar in its crystalline form because the charges are evenly distributed across the lattice structure. However, when dissolved in water, it dissociates into Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions, exhibiting polar behavior in solution.
📌 Note: While NaCl is nonpolar in its solid state, its ions behave as polar entities in aqueous solutions.
Comparing NaCl with Other Compounds

NaCl vs. Covalent Compounds
Unlike covalent compounds like water (H₂O), which are polar due to their molecular geometry and electronegativity differences, NaCl’s ionic nature sets it apart. The table below highlights the differences:
| Compound | Type of Bonding | Polarity |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | Ionic | Nonpolar (solid), Polar (solution) |
| H₂O | Covalent | Polar |

Practical Implications of NaCl’s Polarity
Understanding NaCl's polarity is essential in various applications, including:
- Chemistry: Predicting solubility and reactions in different solvents.
- Biology: Role in cellular processes and osmoregulation.
- Industry: Use in food preservation and chemical manufacturing.
In summary, NaCl is nonpolar in its solid crystalline form due to its ionic lattice structure. However, when dissolved, it exhibits polar behavior due to the separation of ions. This dual nature highlights the importance of context in determining polarity. Whether you're studying chemistry or applying it in real-world scenarios, understanding is NaCl polar or nonpolar is fundamental.
Is NaCl polar or nonpolar in water?
+In water, NaCl dissociates into Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions, exhibiting polar behavior due to the separation of charges.
Why is NaCl considered nonpolar in its solid form?
+NaCl is nonpolar in its solid form because the charges are evenly distributed across its ionic lattice structure.
How does the polarity of NaCl affect its solubility?
+In its solid form, NaCl is nonpolar, but its ions become polar in solution, making it highly soluble in polar solvents like water.
is nacl polar or nonpolar, nacl polarity, ionic compounds, chemical bonding, solubility, polar vs nonpolar, molecular structure, electronegativity, covalent compounds, chemical properties.



