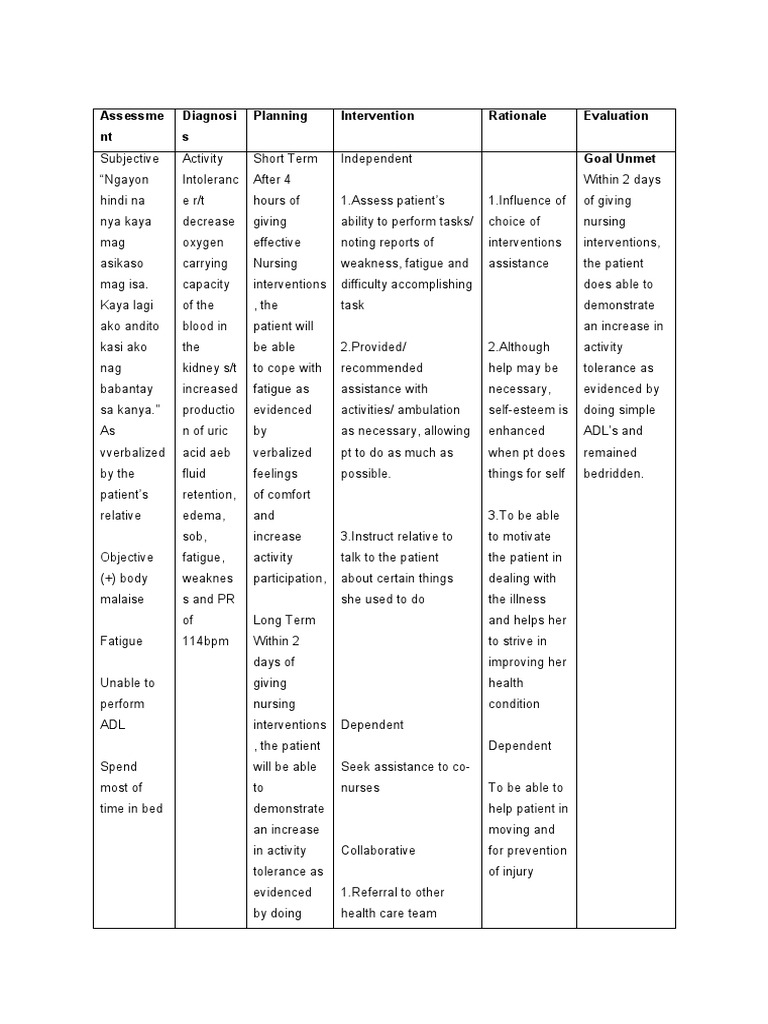
Effective Nursing Care Plan for Hypoxia Management
<!DOCTYPE html>
Hypoxia, a condition characterized by inadequate oxygen supply to tissues, requires prompt and effective nursing care to prevent complications and ensure patient recovery. Whether you’re a nursing professional or a caregiver, understanding the nuances of hypoxia management is crucial. This guide provides a comprehensive nursing care plan tailored for hypoxia management, ensuring optimal patient outcomes. (hypoxia management, nursing care plan, oxygen therapy)
Understanding Hypoxia: Causes and Symptoms

Hypoxia can result from various factors, including respiratory disorders, cardiovascular issues, or environmental conditions. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, rapid breathing, confusion, and bluish skin discoloration (cyanosis). Recognizing these signs early is essential for timely intervention. (hypoxia causes, hypoxia symptoms, cyanosis)
Assessing the Patient: Key Steps in Hypoxia Management

A thorough patient assessment is the foundation of an effective nursing care plan. This includes evaluating vital signs, oxygen saturation levels, and respiratory patterns. Utilize tools like pulse oximetry and arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis for accurate monitoring. (patient assessment, pulse oximetry, ABG analysis)
Steps for Patient Assessment:
- Monitor oxygen saturation (SpO2) levels regularly.
- Assess respiratory rate, depth, and effort.
- Evaluate mental status for signs of confusion or agitation.
📌 Note: Continuous monitoring is critical for patients with severe hypoxia to detect any deterioration promptly.
Implementing Oxygen Therapy: Best Practices

Oxygen therapy is a cornerstone of hypoxia management. The goal is to maintain adequate oxygen levels while avoiding complications like oxygen toxicity. Nurses must select the appropriate delivery method (e.g., nasal cannula, mask) and adjust flow rates based on patient needs. (oxygen therapy, nasal cannula, oxygen toxicity)
| Oxygen Delivery Method | Flow Rate Range | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Nasal Cannula | 1-6 L/min | Mild to moderate hypoxia |
| Simple Face Mask | 5-10 L/min | Moderate to severe hypoxia |

Monitoring and Adjusting the Care Plan

Effective hypoxia management requires ongoing evaluation and adjustments to the care plan. Nurses should reassess oxygen saturation, respiratory status, and patient comfort regularly. Document all findings and communicate changes to the healthcare team. (care plan adjustments, patient monitoring, documentation)
Checklist for Hypoxia Management:
- Assess oxygen saturation every 1-2 hours.
- Monitor for signs of oxygen toxicity (e.g., coughing, chest pain).
- Educate patients on proper use of oxygen equipment.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team for treatment modifications.
Managing hypoxia effectively requires a combination of thorough assessment, appropriate oxygen therapy, and continuous monitoring. By following this nursing care plan, healthcare professionals can ensure patients receive the best possible care, promoting recovery and preventing complications. (nursing care plan, hypoxia management, patient recovery)
What are the early signs of hypoxia?
+Early signs include shortness of breath, rapid breathing, confusion, and bluish skin discoloration (cyanosis). (hypoxia symptoms, cyanosis)
How often should oxygen saturation be monitored?
+Oxygen saturation should be monitored every 1-2 hours, especially in patients with severe hypoxia. (patient monitoring, oxygen saturation)
What is the risk of oxygen toxicity?
+Oxygen toxicity can cause symptoms like coughing, chest pain, and respiratory distress, especially with prolonged high-flow oxygen therapy. (oxygen toxicity, respiratory distress)



