Essential Nursing Metric Conversion Table for Accurate Dosages

<!DOCTYPE html>
Accurate dosage calculations are critical in nursing to ensure patient safety and effective treatment. Nurses frequently encounter metric conversions in their daily practice, making it essential to master these skills. Whether you're converting units for medication administration or interpreting lab results, a reliable nursing metric conversion table is an indispensable tool. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of essential conversions, tips for accuracy, and practical examples to enhance your confidence in clinical settings.
Why Metric Conversions Matter in Nursing

Metric conversions are fundamental in nursing because medications and measurements are often prescribed in different units. Errors in conversions can lead to serious consequences, including underdosing or overdosing. By understanding metric conversions for nurses, you can ensure precise calculations and deliver safe patient care. Common units such as milligrams (mg), micrograms (mcg), liters (L), and milliliters (mL) are frequently used, making proficiency in these conversions a necessity.
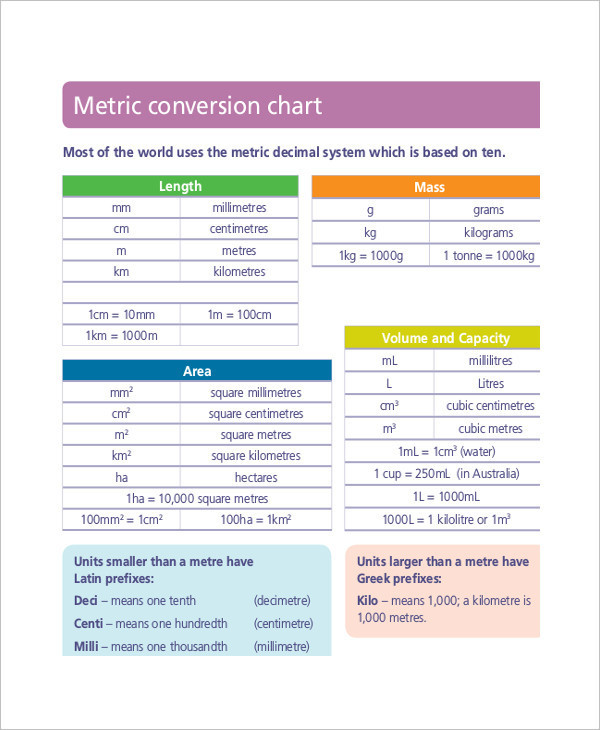
Essential Nursing Metric Conversion Table

Below is a detailed nursing metric conversion table to help you accurately convert units in clinical practice:
| From Unit | To Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Milligrams (mg) | Grams (g) | 1 g = 1000 mg |
| Micrograms (mcg) | Milligrams (mg) | 1 mg = 1000 mcg |
| Liters (L) | Milliliters (mL) | 1 L = 1000 mL |
| Kilograms (kg) | Grams (g) | 1 kg = 1000 g |
| Cubic Centimeters (cc) | Milliliters (mL) | 1 cc = 1 mL |
Tips for Accurate Dosage Calculations

Mastering dosage calculations in nursing requires practice and attention to detail. Here are some tips to ensure accuracy:
- Always double-check your conversions using a reliable nursing conversion chart.
- Use the same unit system throughout your calculations to avoid confusion.
- Round off decimals appropriately based on clinical guidelines.
- Practice regularly with sample problems to build confidence.
📌 Note: Always verify your calculations with a second source or colleague to minimize errors.
Practical Examples of Metric Conversions

Let’s apply the nursing metric conversion table to real-world scenarios:
- Convert 500 mg to grams: 500 mg ÷ 1000 = 0.5 g.
- Convert 2 L to milliliters: 2 L × 1000 = 2000 mL.
- Convert 750 mcg to milligrams: 750 mcg ÷ 1000 = 0.75 mg.
Checklist for Safe Dosage Administration

Follow this checklist to ensure safe and accurate dosage administration:
- Verify the medication and dosage prescribed.
- Use the nursing metric conversion table for accurate unit conversions.
- Double-check your calculations before administration.
- Document the dosage and administration time accurately.
Mastering metric conversions for nurses is essential for safe and effective patient care. By utilizing the provided nursing conversion chart and following best practices, you can confidently perform dosage calculations and ensure positive patient outcomes. (nursing metric conversion table, dosage calculations in nursing, metric conversions for nurses)
Why are metric conversions important in nursing?
+Metric conversions ensure accurate medication dosages and measurements, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing patient safety.
How can I improve my dosage calculation skills?
+Practice regularly with a nursing metric conversion table, use sample problems, and always double-check your calculations.
What are common units used in nursing?
+Common units include milligrams (mg), micrograms (mcg), liters (L), milliliters (mL), and kilograms (kg).



