Orbital Diagram of Mn: Visualizing Electron Configuration

Understanding the orbital diagram of Mn (Manganese) is crucial for anyone studying chemistry, especially electron configurations. This visual representation simplifies the complex arrangement of electrons in manganese atoms, making it easier to grasp its chemical behavior.
Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about electron configuration of Mn, this guide will walk you through the essentials, ensuring clarity and depth.
What is an Orbital Diagram?
An orbital diagram is a visual tool used to represent the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. It follows the principles of the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule. For Mn (Manganese), with an atomic number of 25, the orbital diagram illustrates how its 25 electrons are distributed across different energy levels and subshells.
💡 Note: Orbital diagrams are particularly useful for understanding elements with unique electron configurations, like manganese.
Electron Configuration of Mn

The electron configuration of Mn is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁵. This notation shows that manganese has electrons in the 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, and 3d orbitals. The 4s orbital is filled before the 3d orbital, which is a common exception in transition metals.
Orbital Diagram of Mn: Step-by-Step
- 1s Orbital: Fill the 1s orbital with 2 electrons (represented as ↑↓).
- 2s and 2p Orbitals: Add 2 electrons to the 2s orbital and 6 electrons to the 2p orbitals.
- 3s and 3p Orbitals: Place 2 electrons in the 3s orbital and 6 electrons in the 3p orbitals.
- 4s Orbital: Fill the 4s orbital with 2 electrons.
- 3d Orbital: Distribute the remaining 5 electrons in the 3d orbitals, following Hund’s rule (one electron per orbital before pairing).
| Orbital | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|
| 1s | ↑↓ |
| 2s | ↑↓ |
| 2p | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 3s | ↑↓ |
| 3p | ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
| 4s | ↑↓ |
| 3d | ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ |

✨ Note: The 3d orbitals are filled with single electrons first, demonstrating Hund’s rule in action.
Why is the Orbital Diagram of Mn Important?

The orbital diagram of Mn is essential for understanding its chemical properties, reactivity, and bonding behavior. Manganese’s unique electron configuration, particularly its half-filled 3d subshell, makes it highly reactive and versatile in chemical reactions.
- Chemical Reactivity: The presence of unpaired electrons in the 3d orbital contributes to manganese’s ability to form multiple oxidation states.
- Magnetic Properties: Unpaired electrons also make manganese paramagnetic.
- Industrial Applications: Manganese is widely used in steel production, batteries, and alloys due to its properties derived from its electron configuration.
Checklist for Creating an Orbital Diagram

- Step 1: Identify the atomic number of the element (Mn = 25).
- Step 2: Follow the Aufbau principle to fill orbitals in order of increasing energy.
- Step 3: Apply the Pauli exclusion principle (maximum 2 electrons per orbital).
- Step 4: Use Hund’s rule to fill degenerate orbitals with single electrons first.
- Step 5: Verify the total number of electrons matches the atomic number.
Wrapping Up
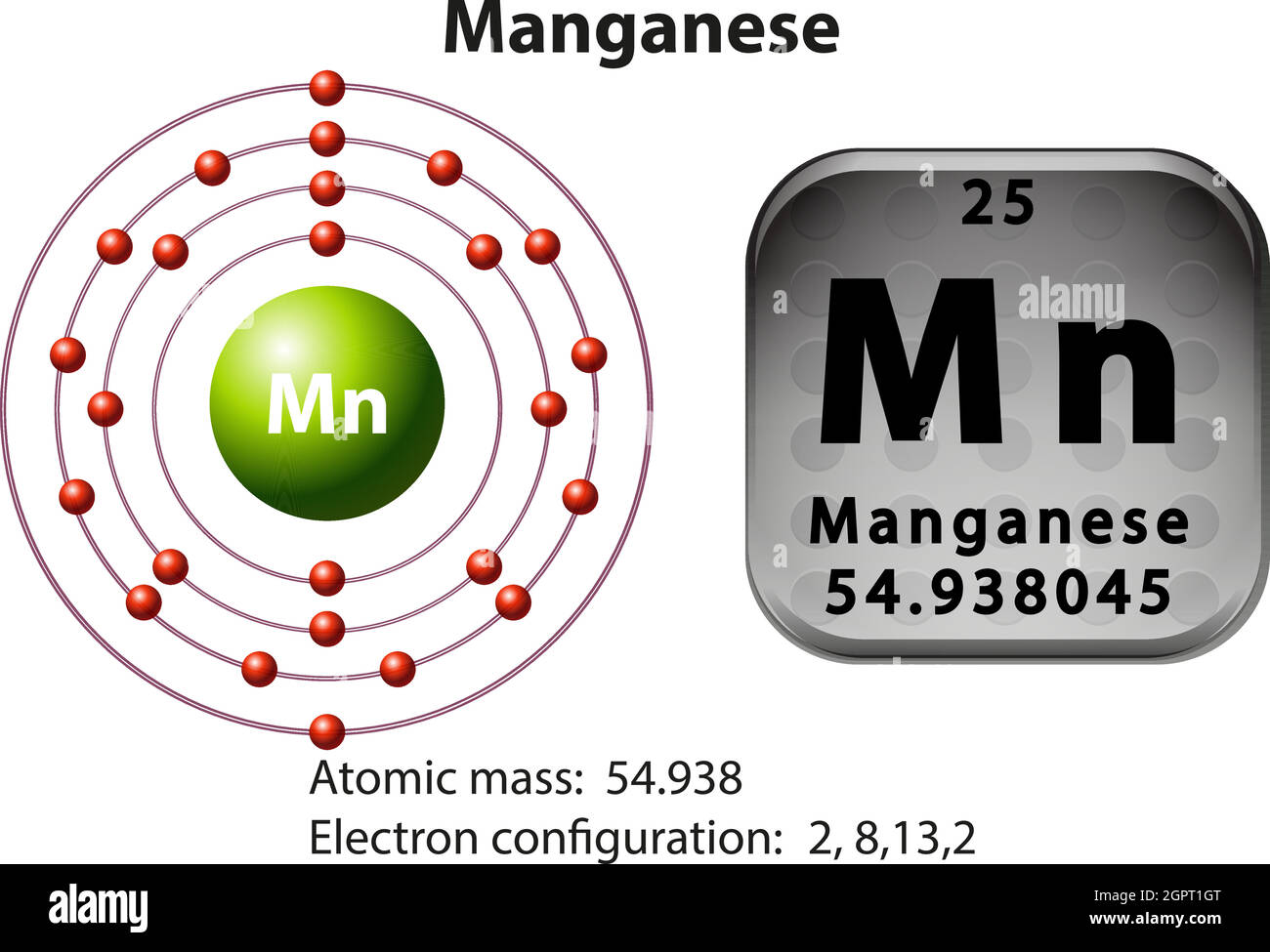
The orbital diagram of Mn provides a clear, visual understanding of its electron configuration, shedding light on its chemical and physical properties. By mastering this concept, you’ll gain deeper insights into manganese’s role in chemistry and its practical applications. Whether you’re studying for exams or exploring advanced chemistry, this guide ensures you’re well-equipped to tackle the topic.
What is the electron configuration of Mn?
+The electron configuration of Mn is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁵.
Why is the 4s orbital filled before the 3d orbital in Mn?
+The 4s orbital has lower energy than the 3d orbital, so it is filled first according to the Aufbau principle.
How does the orbital diagram of Mn explain its magnetic properties?
+The unpaired electrons in the 3d orbitals make Mn paramagnetic, contributing to its magnetic behavior.
electron configuration of Mn,orbital diagram of Mn,Manganese electron configuration,Manganese orbital diagram,Aufbau principle,Hund’s rule,Pauli exclusion principle


