Understanding the Size of Red Blood Cells: A Quick Guide

<!DOCTYPE html>
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, play a crucial role in transporting oxygen throughout the body. Understanding their size is essential for diagnosing various health conditions and ensuring optimal blood function. This guide will explore the dimensions of red blood cells, their significance, and how they impact overall health. Whether you're a medical professional or simply curious, this post will provide valuable insights into the microscopic world of these vital cells, (red blood cell size, erythrocyte dimensions, blood cell measurements)
What is the Average Size of a Red Blood Cell?

The average diameter of a red blood cell is approximately 6-8 micrometers (µm). This size allows them to navigate through tiny capillaries efficiently, ensuring oxygen delivery to all tissues. Their biconcave shape further enhances flexibility, enabling them to deform and pass through narrow vessels. (red blood cell diameter, biconcave shape, oxygen delivery)
Why Does Red Blood Cell Size Matter?
Red blood cell size is a critical indicator of health. Abnormalities in size can signal underlying conditions such as anemia or malnutrition. For instance:
- Microcytosis: Smaller than normal red blood cells, often linked to iron deficiency anemia.
- Macrocytosis: Larger than normal red blood cells, which may indicate vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
Factors Affecting Red Blood Cell Size

Several factors influence the size of red blood cells, including:
- Nutrition: Deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, or folate can alter cell size.
- Genetics: Certain genetic disorders, like thalassemia, affect red blood cell production and size.
- Disease: Conditions such as kidney disease or liver disorders can impact cell dimensions.
How is Red Blood Cell Size Measured?
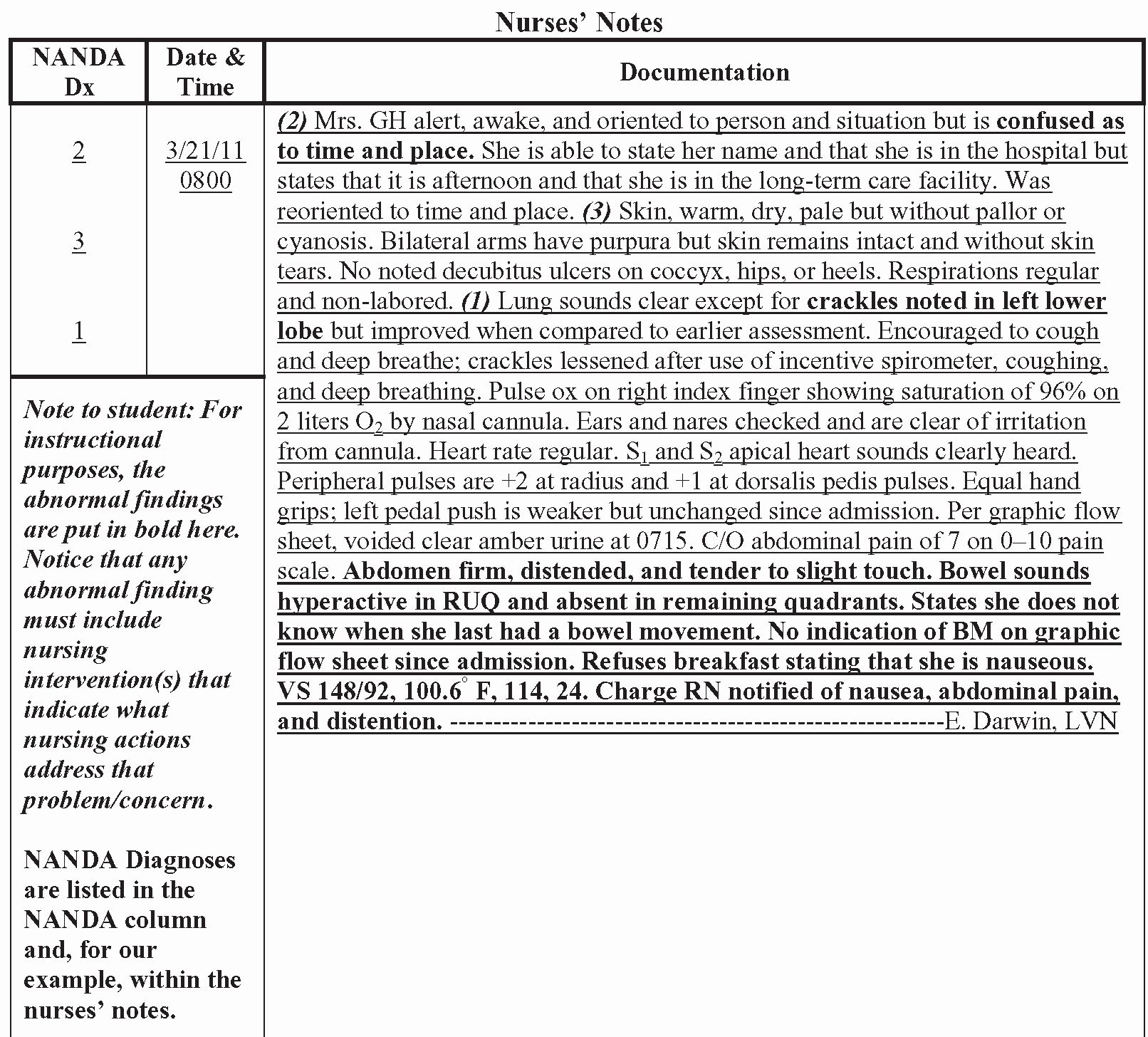
Red blood cell size is typically measured using a complete blood count (CBC) test. Key parameters include:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) | Average volume of red blood cells, measured in femtoliters (fL). |
| Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) | Measures variation in red blood cell size, indicating uniformity. |

These measurements help diagnose size-related disorders. (CBC test, MCV, RDW)
💡 Note: Regular blood tests can help monitor red blood cell size and detect abnormalities early.
Understanding the size of red blood cells is vital for assessing overall health and diagnosing related conditions. From their average diameter to the factors affecting their size, this knowledge empowers both individuals and healthcare providers. By staying informed and monitoring key parameters, you can ensure optimal blood function and well-being. (red blood cell health, blood function, health monitoring)
What is the normal size of a red blood cell?
+The average diameter of a red blood cell is 6-8 micrometers (µm).
What causes red blood cells to be smaller than normal?
+Smaller red blood cells, or microcytosis, are often caused by iron deficiency anemia.
How is red blood cell size measured?
+Red blood cell size is measured using parameters like Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) in a complete blood count (CBC) test.