Spatial vs Temporal Summation: Unraveling the Brain's Signal Secrets

The human brain is a marvel of complexity, constantly processing signals to help us navigate the world. Two key processes, spatial summation and temporal summation, play critical roles in how neurons communicate. Understanding these mechanisms not only sheds light on brain function but also has implications for neuroscience research and neurological health.
What is Spatial Summation?
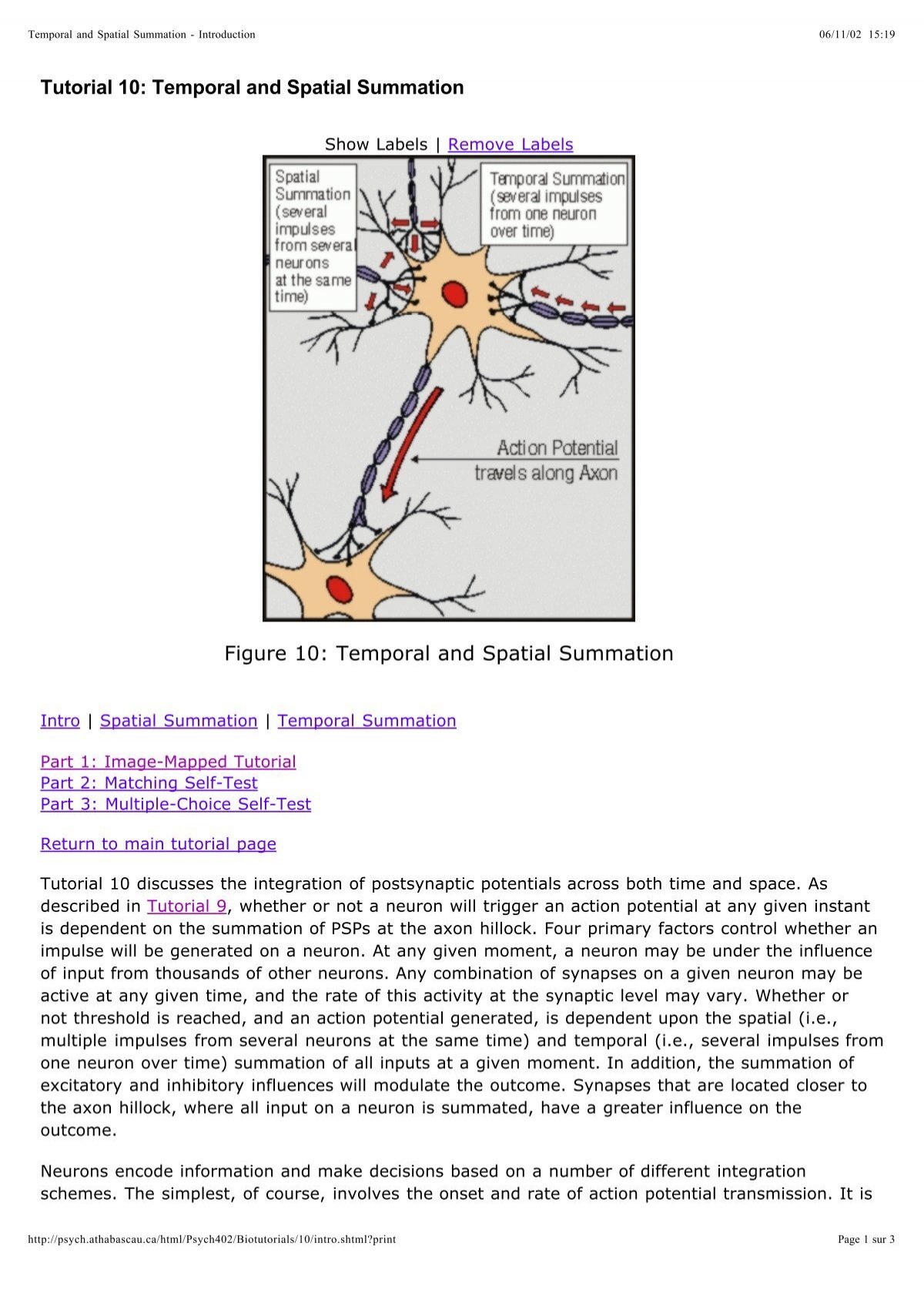
Spatial summation occurs when multiple neurons stimulate the same postsynaptic neuron simultaneously. This combined input increases the likelihood of the neuron reaching its threshold and firing an action potential. Think of it as a group effort where several signals work together to amplify the message.
Key Features of Spatial Summation:
- Multiple Inputs: Signals from different presynaptic neurons converge on a single postsynaptic neuron.
- Simultaneous Activation: The signals arrive at the same time, creating a cumulative effect.
- Threshold Achievement: The combined strength of the signals helps the neuron reach its firing threshold.
💡 Note: Spatial summation is essential for processes like sensory integration, where inputs from various sources are combined to form a coherent perception.
What is Temporal Summation?

Temporal summation, on the other hand, involves repeated signals from a single presynaptic neuron arriving at the postsynaptic neuron in quick succession. Each signal builds upon the previous one, increasing the postsynaptic potential until the neuron fires.
Key Features of Temporal Summation:
- Single Input Source: Signals originate from one presynaptic neuron.
- Rapid Succession: The signals arrive close together in time.
- Cumulative Effect: Each signal adds to the previous one, gradually reaching the threshold.
💡 Note: Temporal summation is crucial for maintaining prolonged neuronal activity, such as during sustained muscle contractions.
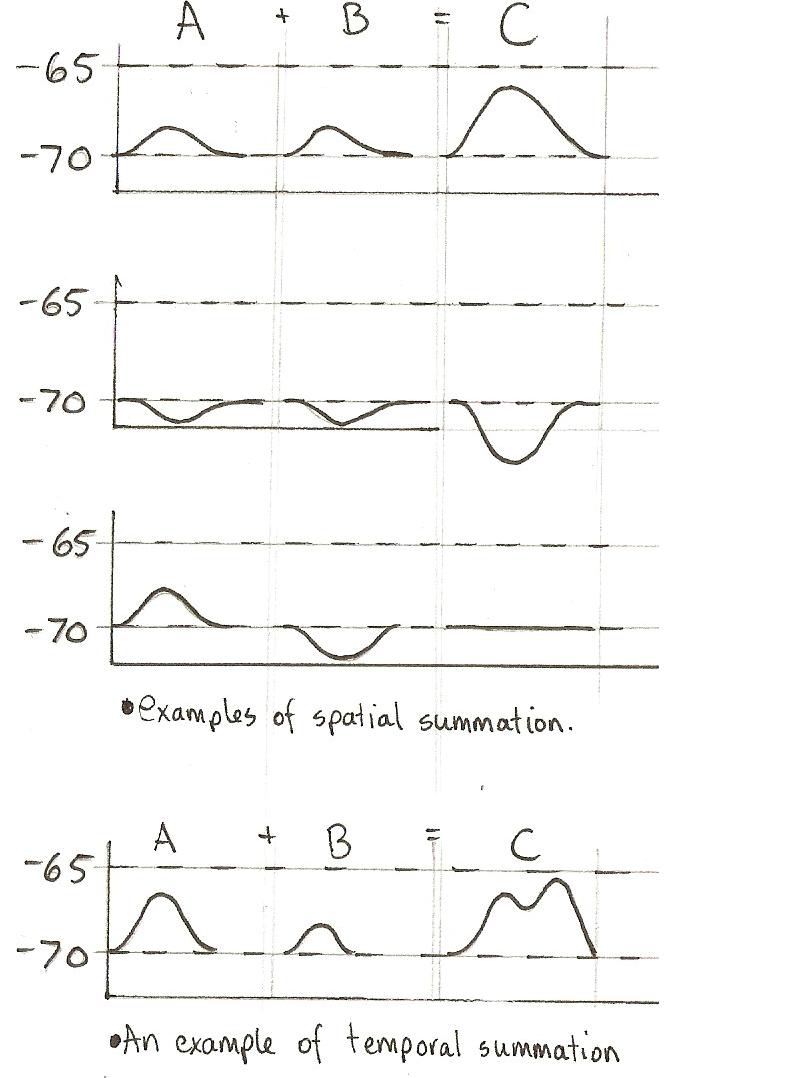
Comparing Spatial and Temporal Summation

To better understand the differences, let’s compare these two processes in a table:
| Feature | Spatial Summation | Temporal Summation |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Inputs | Multiple neurons | Single neuron |
| Timing of Signals | Simultaneous | In rapid succession |
| Mechanism | Summation of simultaneous inputs | Summation of repeated inputs |

Why Does This Matter?
Understanding spatial and temporal summation is vital for neuroscientists, medical professionals, and anyone interested in how the brain processes information. These mechanisms underpin everything from sensory perception to motor control.
Applications in Neuroscience:
- Research: Studying summation helps researchers understand neuronal communication.
- Health: Disorders like epilepsy or chronic pain may involve abnormal summation processes.
- Technology: Insights into summation inspire advancements in neuroprosthetics and brain-computer interfaces.
Checklist for Understanding Summation:
- Identify the Source: Determine if signals come from multiple neurons (spatial) or a single neuron (temporal).
- Analyze Timing: Check if signals arrive simultaneously (spatial) or in quick succession (temporal).
- Assess Threshold: Understand how the combined signals help reach the firing threshold.
Final Thoughts
Spatial and temporal summation are fundamental to neuronal communication, each playing a unique role in how the brain processes and transmits information. By unraveling these mechanisms, we gain deeper insights into brain function and its implications for health and technology. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about the brain, understanding these processes is a step toward appreciating the complexity of our most vital organ.
What is the main difference between spatial and temporal summation?
+Spatial summation involves multiple neurons stimulating a single postsynaptic neuron simultaneously, while temporal summation involves repeated signals from a single neuron arriving in quick succession.
Why is spatial summation important?
+Spatial summation is crucial for integrating signals from various sources, enabling processes like sensory perception and complex neural computations.
How does temporal summation contribute to brain function?
+Temporal summation allows for sustained neuronal activity, which is essential for prolonged actions like muscle contractions or maintaining focus.
neuronal communication,brain function,neuroscience research,sensory perception,motor control,neuroprosthetics,brain-computer interfaces,epilepsy,chronic pain.



