Strep vs. Staph: Understanding These Common Bacteria

When it comes to bacterial infections, Strep and Staph are two common culprits that often cause confusion. While both are bacteria, they differ in their types, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. Whether you're dealing with a sore throat or a skin infection, knowing whether it’s Strep or Staph can make all the difference in your recovery. (Strep throat, Staph infection, bacterial infections)
What is Strep Bacteria?

Strep, short for Streptococcus, is a group of bacteria responsible for various infections, most notably Strep throat. This bacterial infection affects the throat and tonsils, causing symptoms like severe throat pain, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Strep throat is highly contagious and commonly spreads through respiratory droplets. (Streptococcus, Strep throat symptoms, contagious infections)
Common Strep Infections
- Strep Throat: The most common Strep infection, characterized by a sore throat and white patches on the tonsils.
- Skin Infections: Strep can also cause impetigo, a skin condition marked by red sores and blisters.
- Scarlet Fever: A complication of Strep throat, accompanied by a rash and high fever.
What is Staph Bacteria?
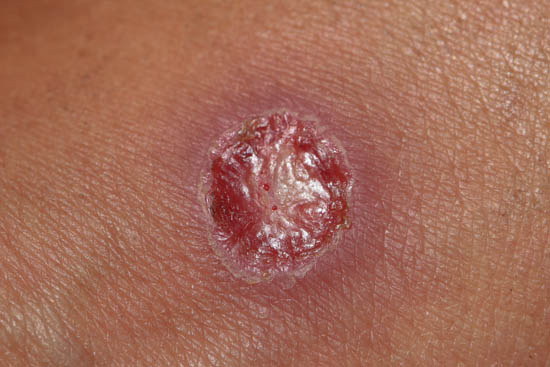
Staph, or Staphylococcus, is another common bacterium that resides on the skin and in the nose. While often harmless, certain strains like MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus) can cause serious infections. Staph infections typically manifest as skin boils, abscesses, or cellulitis. (Staphylococcus, MRSA, skin infections)
Common Staph Infections
- Skin Abscesses: Painful, pus-filled bumps that require drainage.
- Cellulitis: A skin infection causing redness, swelling, and warmth.
- Food Poisoning: Certain Staph strains produce toxins that lead to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
| Feature | Strep | Staph |
|---|---|---|
| Common Infection Site | Throat, Tonsils | Skin, Soft Tissues |
| Symptoms | Sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes | Skin boils, abscesses, redness |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (e.g., penicillin) | Antibiotics (e.g., vancomycin for MRSA) |

⚠️ Note: Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections.
How to Prevent Strep and Staph Infections

Prevention is key when it comes to bacterial infections. Simple hygiene practices can significantly reduce your risk of contracting Strep or Staph. (Infection prevention, hygiene tips)
Prevention Tips
- Wash Hands Frequently: Use soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Don’t share utensils, towels, or razors.
- Keep Wounds Clean: Cover cuts and scrapes with clean bandages.
- Practice Good Respiratory Hygiene: Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
Quick Checklist: Strep vs. Staph
- Strep: Throat infections, Strep throat, antibiotics like penicillin.
- Staph: Skin infections, MRSA, antibiotics like vancomycin.
- Prevention: Handwashing, avoiding shared items, wound care.
Understanding the differences between Strep and Staph bacteria is essential for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. While Strep primarily affects the throat, Staph targets the skin and soft tissues. Both require prompt medical attention, especially in severe cases. By practicing good hygiene and being aware of the signs, you can reduce your risk of infection and stay healthy. (Strep vs. Staph, bacterial infections, infection prevention)
Can Strep throat turn into a Staph infection?
+
No, Strep throat and Staph infections are caused by different bacteria. However, secondary infections can occur if left untreated.
How long does it take to recover from Strep throat?
+
With proper antibiotic treatment, symptoms usually improve within 2-3 days, but it’s important to complete the full course of medication.
Is MRSA contagious?
+
Yes, MRSA can spread through skin-to-skin contact or by touching contaminated surfaces. Proper hygiene is crucial to prevent transmission.