Mastering Strong Acid Weak Base Titration: Tips & Tricks

Mastering strong acid weak base titration is essential for anyone working in chemistry labs, whether you're a student or a professional. This process involves carefully measuring the pH changes as a strong acid neutralizes a weak base, ultimately determining the concentration of the base. By understanding the principles and techniques, you can achieve accurate results and avoid common pitfalls. In this guide, we’ll explore tips and tricks to help you excel in this critical lab procedure, ensuring precision and efficiency in your experiments. (strong acid weak base titration,titration techniques,lab precision)
Understanding the Basics of Strong Acid Weak Base Titration

Before diving into the tips and tricks, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of strong acid weak base titration. This titration relies on the reaction between a strong acid (e.g., HCl) and a weak base (e.g., NH₃), producing a salt and water. The key is monitoring the pH shift using an indicator or a pH meter. Understanding the titration curve and the equivalence point is vital for accurate measurements. (titration curve,equivalence point,pH monitoring)
Essential Tools and Reagents for Titration
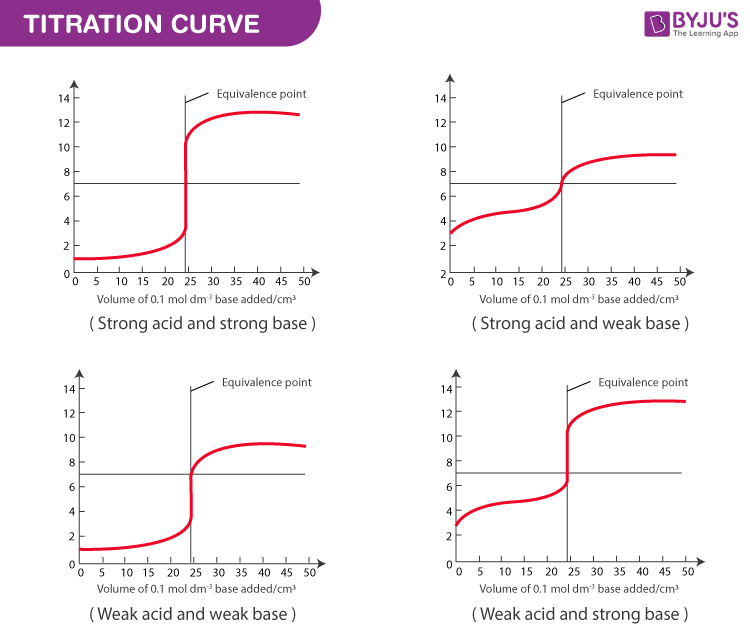
To perform a successful strong acid weak base titration, you’ll need the right tools and reagents. Here’s a checklist:
- Burette: For precise acid delivery.
- pH Meter or Indicator: To monitor pH changes.
- Conical Flask: To hold the weak base solution.
- Standardized Strong Acid: Typically HCl or H₂SO₄.
- Weak Base Solution: The analyte being tested.
Ensuring all equipment is clean and calibrated is critical for reliable results. (burette,pH meter,conical flask)
Step-by-Step Titration Process

Follow these steps for a seamless strong acid weak base titration:
- Prepare Solutions: Standardize the strong acid and prepare the weak base solution.
- Set Up Equipment: Fill the burette with the acid and place the base in the conical flask.
- Add Indicator: Use a suitable pH indicator or calibrate the pH meter.
- Titrate Slowly: Add acid dropwise while stirring until the endpoint is reached.
- Record Results: Note the volume of acid used and calculate the base concentration.
💡 Note: Always rinse the burette with the acid solution before use to avoid contamination.
(titration steps,endpoint detection,acid standardization)
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Titration

Even experienced chemists can make errors in strong acid weak base titration. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
- Incorrect Endpoint Detection: Misjudging the endpoint can lead to inaccurate results.
- Improper Stirring: Inadequate mixing can cause slow or uneven pH changes.
- Using Uncalibrated Equipment: Always calibrate your pH meter and burette for precision.
Avoiding these mistakes will significantly improve your titration accuracy. (endpoint errors,stirring techniques,equipment calibration)
Advanced Tips for Precision in Titration

To take your strong acid weak base titration skills to the next level, consider these advanced tips:
- Use a Digital Burette: For even greater accuracy in acid delivery.
- Automate the Process: Titration systems can reduce human error.
- Perform Blank Titrations: Account for any impurities in the reagents.
These techniques can enhance both efficiency and reliability in your experiments. (digital burette,automated titration,blank titration)
Mastering strong acid weak base titration requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. By understanding the basics, using the right tools, and avoiding common mistakes, you can achieve precise and reliable results. Incorporate the advanced tips to further refine your technique and elevate your lab work. (titration mastery,lab skills,precision techniques)
What is the equivalence point in strong acid weak base titration?
+
The equivalence point is where the moles of acid and base are stoichiometrically equal, neutralizing each other completely.
How do I choose the right pH indicator for titration?
+
Select an indicator with a pH range that includes the equivalence point of your titration, typically phenolphthalein for strong acid-weak base reactions.
Why is stirring important during titration?
+
Stirring ensures uniform mixing of the acid and base, leading to accurate and consistent pH changes throughout the titration.



