Subjective vs Objective Data: Key Differences Explained Mastering Subjective & Objective Data in Research How to Distinguish Subjective from Objective Data Understanding Subjective and Objective Data Essentials Subjective vs Objective Data: What’s the Difference?

In the world of research and data analysis, understanding the difference between subjective vs objective data is crucial. These two types of data play distinct roles in shaping insights, making decisions, and drawing conclusions. Whether you’re a researcher, a student, or a professional, mastering the concepts of subjective and objective data can significantly enhance the quality of your work. This blog post will explore the key differences between subjective and objective data, provide practical tips for distinguishing them, and offer essential insights to help you navigate their use effectively.
What is Subjective Data?

Subjective data refers to information based on personal opinions, feelings, or interpretations. It is inherently biased and varies from person to person. For example, asking someone to rate their pain level on a scale of 1 to 10 is subjective because it relies on their individual perception. Subjective data is valuable in qualitative research, where understanding perspectives and experiences is key.
📌 Note: Subjective data is essential for capturing human emotions and experiences but should be used cautiously in quantitative studies.
What is Objective Data?

Objective data, on the other hand, is factual, measurable, and verifiable. It is based on observable facts and can be confirmed by multiple sources. For instance, measuring a patient’s blood pressure or recording the temperature of a room are examples of objective data. This type of data is critical in scientific research, where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
Key Differences Between Subjective and Objective Data
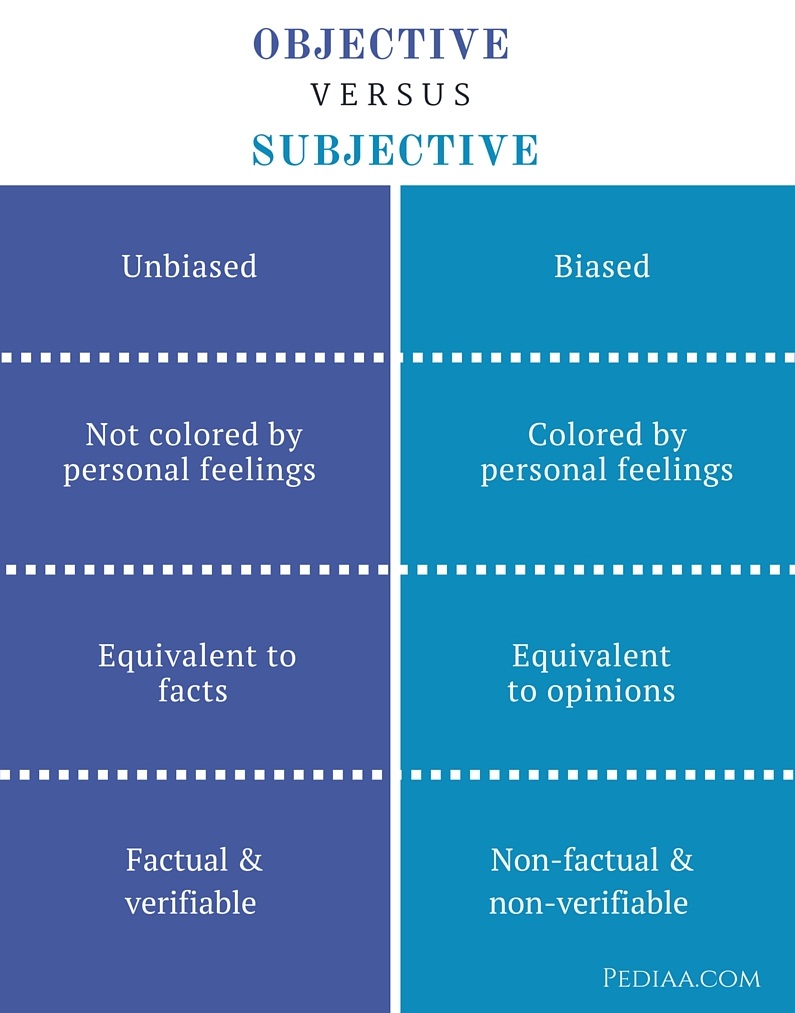
To better understand subjective vs objective data, let’s break down their key differences in a table:
| Aspect | Subjective Data | Objective Data |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Personal opinions, feelings | Observable facts, measurements |
| Reliability | Varies by individual | Consistent and verifiable |
| Use Case | Qualitative research, surveys | Quantitative research, experiments |
| Example | "I feel happy today." | "The room temperature is 25°C." |

How to Distinguish Subjective from Objective Data

Distinguishing between subjective and objective data can sometimes be challenging. Here are some tips to help you identify them:
- Ask if it’s based on opinion or fact: If the data relies on personal feelings or interpretations, it’s likely subjective. If it’s a measurable fact, it’s objective.
- Check for variability: Subjective data varies among individuals, while objective data remains consistent.
- Look for verification: Objective data can be verified by multiple sources, whereas subjective data cannot.
📌 Note: Practice identifying data types by analyzing real-world examples to improve your skills.
Mastering Subjective and Objective Data in Research

To effectively use subjective and objective data in research, consider the following strategies:
- Combine both types: Use subjective data to understand perspectives and objective data to validate findings.
- Clearly label data types: Ensure your research distinguishes between subjective and objective data for transparency.
- Use appropriate methods: Employ qualitative methods for subjective data and quantitative methods for objective data.
Understanding Subjective and Objective Data Essentials
In essence, subjective data captures the human experience, while objective data provides concrete facts. Both are valuable but serve different purposes. By understanding their key differences, you can leverage them effectively in your research, decision-making, and analysis.
Subjective vs Objective Data: What’s the Difference?
To summarize, the main difference lies in their basis and reliability. Subjective data is personal and variable, while objective data is factual and consistent. Mastering these concepts will empower you to conduct more robust and insightful research.
What is an example of subjective data?
+An example of subjective data is a person stating, "I love this movie," as it reflects personal opinion.
Can subjective data be used in scientific research?
+Yes, subjective data can be used in scientific research, particularly in qualitative studies to understand human experiences.
How can I ensure my research uses objective data effectively?
+Ensure your research uses measurable, verifiable data and employs quantitative methods for analysis.
By now, you should have a clear understanding of subjective vs objective data and how to apply them in various contexts. Remember, both types of data are valuable, and knowing when to use each will enhance the quality and credibility of your work. (subjective vs objective data, subjective and objective data, key differences)