Sun Earth Moon System Model Explained Simply
Understanding the Sun Earth Moon System Model is essential for grasping the dynamics of our solar system. This model explains the relationships between the Sun, Earth, and Moon, including their movements, positions, and interactions. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply curious about astronomy, this guide breaks down the complexities into simple, digestible concepts. By the end of this post, you’ll have a clear understanding of how this system works and its significance in our daily lives, (solar system model, celestial bodies, astronomical concepts)
What is the Sun Earth Moon System Model?
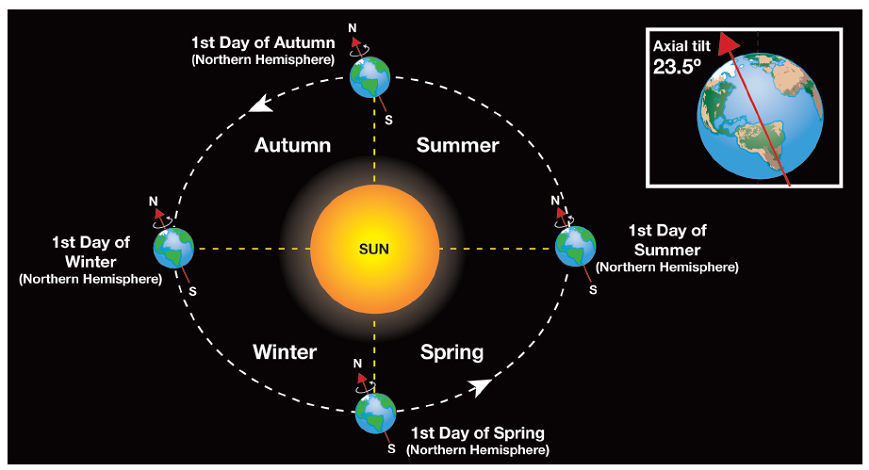
The Sun Earth Moon System Model is a simplified representation of the interactions between the three primary celestial bodies in our immediate cosmic neighborhood. It focuses on their orbits, phases, and gravitational influences. This model is crucial for understanding phenomena like day and night, seasons, tides, and lunar phases, (celestial mechanics, gravitational forces, lunar phases)
Key Components of the Sun Earth Moon System
The Sun: The Center of It All
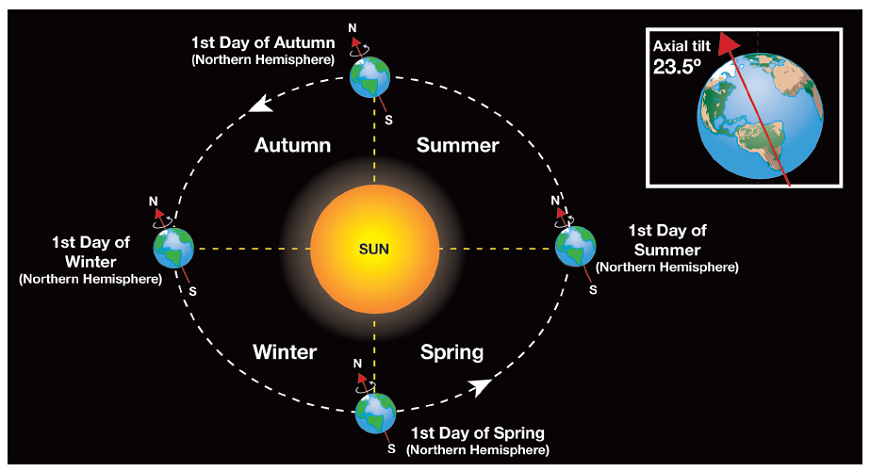
The Sun is the central star of our solar system, providing light, heat, and energy. It holds the Earth and Moon in their orbits through its massive gravitational pull. Without the Sun, life on Earth would not exist, (star system, solar energy, gravitational pull)
Earth: Our Home Planet
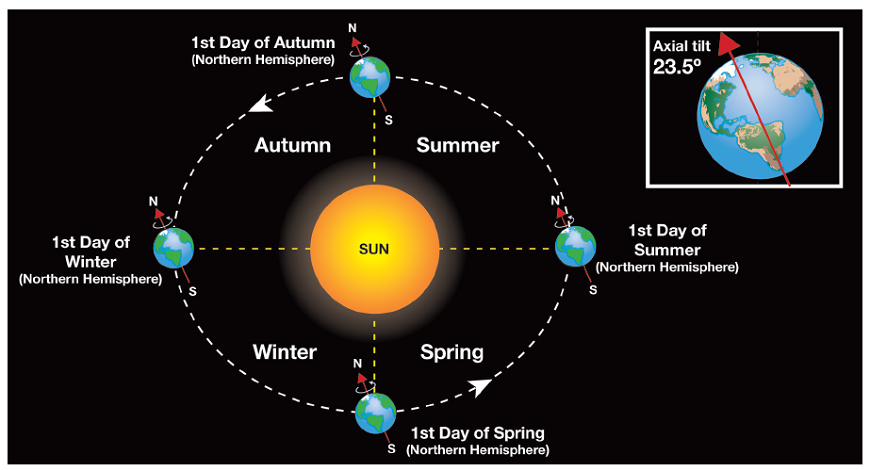
The Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only known planet to support life. It rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and orbits the Sun, creating the yearly cycle of seasons. The Earth’s relationship with the Moon is particularly fascinating, as it influences tides and stabilizes our planet’s rotation, (planet Earth, axial rotation, tidal forces)
The Moon: Earth’s Closest Companion
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite, orbiting our planet while also moving around the Sun alongside Earth. Its phases, such as full moon and new moon, are a result of its position relative to the Earth and Sun. The Moon’s gravitational pull causes ocean tides and affects Earth’s climate, (natural satellite, lunar orbit, ocean tides)
How the Sun Earth Moon System Works

The system operates through a delicate balance of gravitational forces and orbital movements. Here’s a breakdown:
- Orbits: Earth orbits the Sun in an elliptical path, completing one revolution in about 365.25 days. The Moon orbits Earth in approximately 27.3 days.
- Phases: The Moon’s phases occur due to its position relative to the Sun and Earth, blocking or reflecting sunlight in different ways.
- Tides: The Moon’s gravitational pull causes the rise and fall of ocean tides, with the Sun also contributing to this effect.
📌 Note: The Moon’s orbit is not a perfect circle, which affects the intensity of tides during different lunar phases, (orbital mechanics, lunar phases, tidal effects)
Practical Applications of the Sun Earth Moon System Model

Understanding this model has real-world applications, including:
- Agriculture: Farmers use knowledge of seasons and lunar cycles for planting and harvesting.
- Navigation: Sailors and aviators rely on celestial bodies for navigation.
- Renewable Energy: Solar energy systems are designed based on the Sun’s position and movement.
Summary Checklist
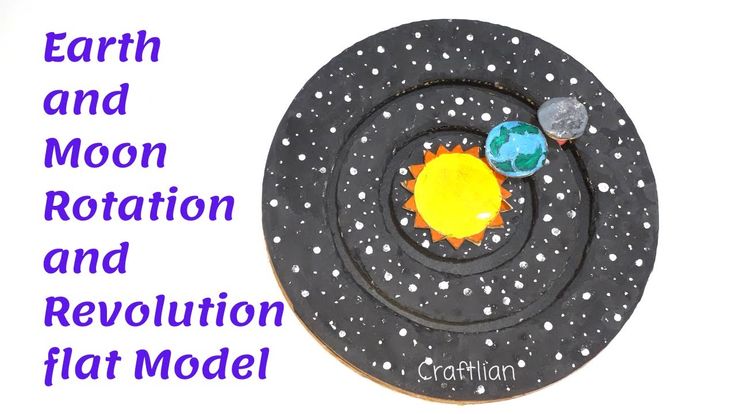
- The Sun is the central star, providing energy and gravitational pull.
- Earth rotates and orbits the Sun, causing day/night and seasons.
- The Moon orbits Earth, causing phases and tides.
- Gravitational forces and orbits are key to the system’s dynamics.
In summary, the Sun Earth Moon System Model is a fundamental concept in astronomy that explains the interactions between these celestial bodies. By understanding their orbits, phases, and gravitational influences, we gain insights into natural phenomena like seasons, tides, and lunar cycles. This knowledge not only satisfies curiosity but also has practical applications in fields like agriculture, navigation, and renewable energy. Whether you’re a student or an enthusiast, mastering this model opens doors to a deeper appreciation of our universe, (astronomy basics, celestial interactions, practical astronomy)
What causes the Moon’s phases?
+
The Moon’s phases occur due to its position relative to the Sun and Earth, affecting how much sunlight is reflected toward us.
How does the Moon affect Earth’s tides?
+
The Moon’s gravitational pull causes the oceans to bulge, creating high and low tides. The Sun also contributes to this effect.
Why does Earth have seasons?
+
Seasons occur due to Earth’s axial tilt, which changes the angle of sunlight reaching different parts of the planet throughout its orbit.