Units of Spring Constant: What Does k Measure?
Understanding the units of the spring constant (k) is crucial for anyone working with springs, whether in physics, engineering, or everyday applications. The spring constant, denoted as *k*, measures the stiffness of a spring and determines how much force is required to deform it. But what exactly does *k* measure, and why is it important? This post will break down the units of the spring constant, its significance, and how it’s applied in real-world scenarios. (spring constant units, spring stiffness, Hooke's Law)
What is the Spring Constant (k)?

The spring constant (k) is a fundamental concept in physics, derived from Hooke’s Law, which states that the force (F) required to extend or compress a spring is directly proportional to the displacement (x):
F = -kx
Here, k quantifies the spring’s resistance to deformation. A higher k value indicates a stiffer spring, while a lower value suggests a more flexible one. (Hooke’s Law, spring force, spring deformation)
Units of the Spring Constant: Breaking It Down

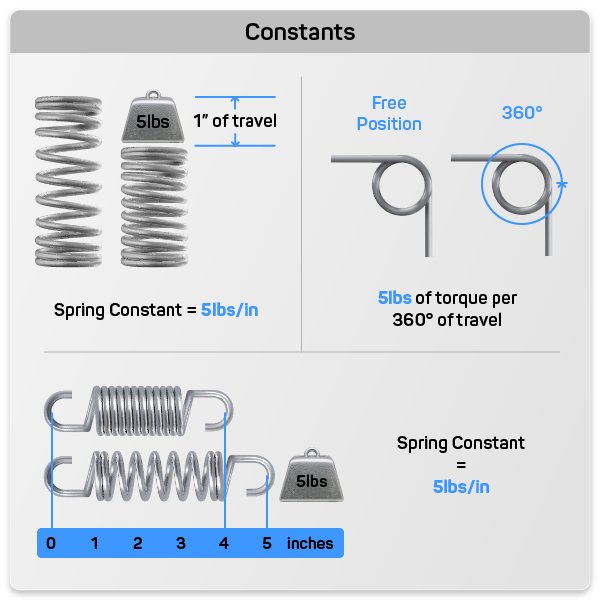
The units of k depend on the measurement system used. In the International System of Units (SI), the units of k are:
N/m (Newtons per meter)
This unit arises because k is defined as the force (F in Newtons) divided by the displacement (x in meters):
k = F / x
For example, if a spring requires 10 N of force to stretch it by 0.5 m, the spring constant is:
k = 10 N / 0.5 m = 20 N/m
📌 Note: In other systems, like the Imperial System, k may be expressed in lbf/in (pounds-force per inch). (SI units, Imperial units, force measurement)
Why Are the Units of k Important?

Understanding the units of k is essential for several reasons:
- Design and Engineering: Engineers use k to select the right spring for applications like automotive suspensions or industrial machinery.
- Physics Experiments: Accurate measurements of k ensure precise results in laboratory experiments.
- Material Science: The spring constant helps analyze material properties, such as elasticity and tensile strength.
Without proper unit knowledge, calculations can lead to errors or inefficient designs. (spring design, material science, engineering applications)
How to Measure the Spring Constant

Measuring k involves applying a known force to a spring and measuring the resulting displacement. Here’s a simple checklist:
- Secure the spring in a fixed position.
- Apply a measurable force (e.g., using weights).
- Measure the displacement accurately.
- Calculate k using the formula k = F / x.
For commercial applications, specialized tools like spring testers provide precise measurements. (spring testing, measurement tools, precision engineering)
The units of the spring constant (*k*) are fundamental to understanding spring behavior and its applications. Whether you’re an engineer, student, or hobbyist, knowing that *k* is measured in N/m (or equivalent units) helps in accurate calculations and effective design. By mastering this concept, you can ensure optimal performance in any spring-related project. (spring constant applications, physics fundamentals, engineering precision)
What does the spring constant (k) measure?
+
The spring constant (k) measures the stiffness of a spring, indicating how much force is needed to deform it by a certain amount.
What are the SI units of the spring constant?
+
The SI units of the spring constant (k) are N/m (Newtons per meter).
How is the spring constant calculated?
+
The spring constant (k) is calculated using the formula k = F / x, where F is the force applied and x is the displacement.



