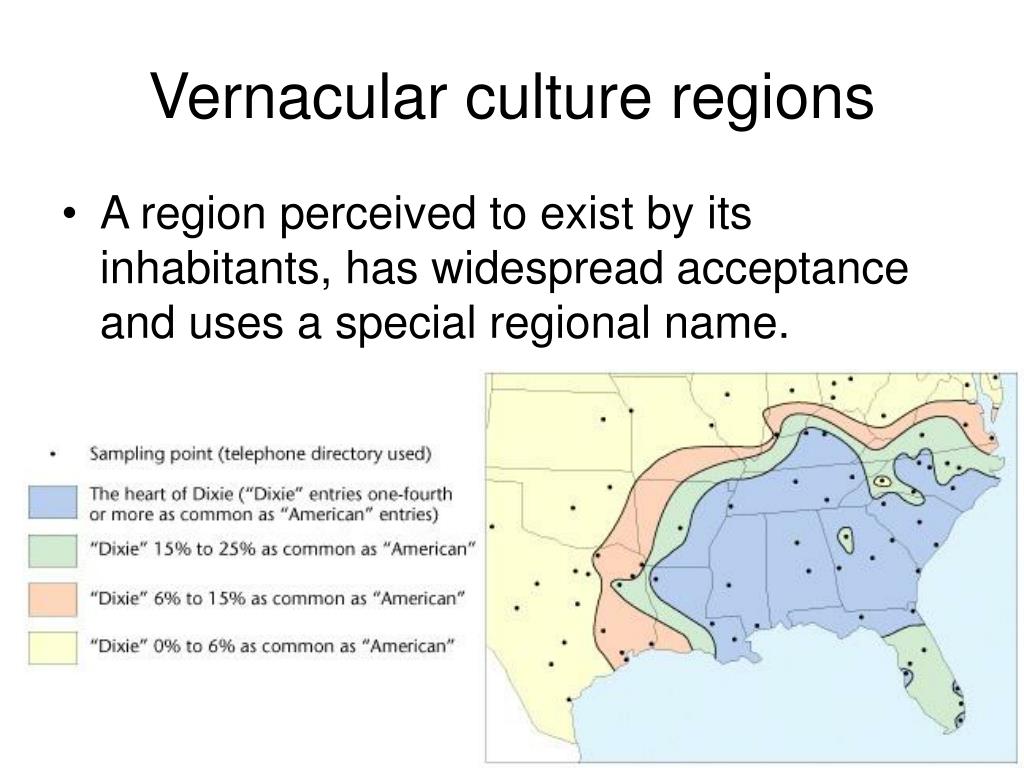
What Is a Vernacular Region? Explained Simply

A vernacular region, often referred to as a perceptual region, is a geographic area defined by people’s perceptions and feelings rather than by formal boundaries. These regions are shaped by cultural, social, and historical factors that resonate with the local population. For example, when someone says “the South” in the United States, they’re referring to a vernacular region defined by shared traditions, dialects, and lifestyles, not just state lines. Understanding vernacular regions helps us grasp how people identify with places and why certain areas hold unique significance.
What Defines a Vernacular Region?

Vernacular regions are characterized by their informal nature and the shared identity of the people within them. Unlike formal regions, which are defined by specific data (like climate or political borders), vernacular regions are subjective and vary based on personal or collective perceptions. Key factors include:
- Cultural Practices: Traditions, festivals, and customs that unify the region.
- Language and Dialect: Unique phrases or accents that locals identify with.
- Historical Significance: Events or heritage that shape the region’s identity.
- Landmarks and Symbols: Iconic places or symbols that represent the area.
📌 Note: Vernacular regions can overlap or change over time as perceptions evolve.
Examples of Vernacular Regions

To better understand vernacular regions, let’s look at a few examples:
1. The Midwest, USA: Known for its agricultural heritage and friendly culture.
2. The Mediterranean: Associated with a relaxed lifestyle, olive groves, and coastal living.
3. The Outback, Australia: Symbolizes rugged terrain and a pioneering spirit.
These regions are not defined by strict borders but by the collective imagination of the people who live in or interact with them.
Why Vernacular Regions Matter
Vernacular regions play a crucial role in shaping local identity and fostering a sense of belonging. They also influence:
- Tourism: Visitors are often drawn to regions based on their perceived charm or uniqueness.
- Marketing: Businesses use regional identities to appeal to specific audiences.
- Community Building: Shared perceptions strengthen local bonds and pride.
How to Identify a Vernacular Region

Here’s a simple checklist to spot a vernacular region:
- Ask Locals: Do they refer to the area by a specific name or describe it with unique traits?
- Look for Symbols: Are there landmarks or traditions that define the region?
- Check Cultural References: Does the area appear in literature, music, or art with distinct characteristics?
Vernacular Regions vs. Formal Regions

While vernacular regions are based on perception, formal regions rely on measurable data. For instance:
| Aspect | Vernacular Region | Formal Region |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Subjective, based on perception | Objective, based on data |
| Example | “The Deep South” | “The Southeast U.S.” |
| Boundaries | Fluid and undefined | Clear and precise |
📌 Note: Both types of regions are important for understanding geography, but they serve different purposes.
Vernacular regions highlight the emotional and cultural connections people have to places, making them a fascinating aspect of geography. By recognizing these regions, we gain insight into how identity, tradition, and perception shape our world. Whether it’s the charm of a rural area or the vibrancy of a city, vernacular regions remind us that geography is as much about people as it is about maps.
What is the difference between a vernacular region and a formal region?
+
A vernacular region is defined by people’s perceptions and cultural identity, while a formal region is based on specific data like climate or political boundaries.
Can vernacular regions change over time?
+
Yes, vernacular regions can evolve as perceptions, cultures, and traditions change.
Why are vernacular regions important?
+
They help us understand local identities, influence tourism, marketing, and foster community pride.



