Biotic Factors Shaping Savanna Ecosystems Explained

Savanna ecosystems are among the most fascinating and diverse environments on Earth, characterized by their unique blend of grasses, scattered trees, and a rich array of wildlife. Biotic factors, or living components, play a crucial role in shaping these ecosystems, influencing everything from soil fertility to predator-prey dynamics. Understanding these factors is essential for conservation efforts, sustainable land management, and appreciating the delicate balance of nature. Whether you're a nature enthusiast, a student, or a conservationist, this guide will explore the key biotic factors that define savanna ecosystems, savanna biodiversity, and ecosystem dynamics.
Key Biotic Factors in Savanna Ecosystems

Savannas are shaped by a variety of biotic factors, each contributing to the ecosystem’s structure and function. Below are the primary living components that play a pivotal role:
Vegetation and Its Role
Vegetation is the backbone of savanna ecosystems, providing food, shelter, and habitat for countless species. Grasses dominate the landscape, while trees like acacias and baobabs are strategically scattered. This mix supports a wide range of herbivores, from elephants to gazelles, and influences the distribution of predators. Savanna vegetation, grassland ecosystems, and plant adaptations are key to understanding this dynamic.
Wildlife Interactions
The interplay between predators and prey is a defining feature of savannas. Lions, cheetahs, and hyenas regulate herbivore populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining ecological balance. Similarly, herbivores like zebras and wildebeests shape vegetation patterns through their feeding habits. These interactions highlight the importance of biodiversity, wildlife conservation, and ecological balance in savanna ecosystems.
The Impact of Biotic Factors on Savanna Dynamics
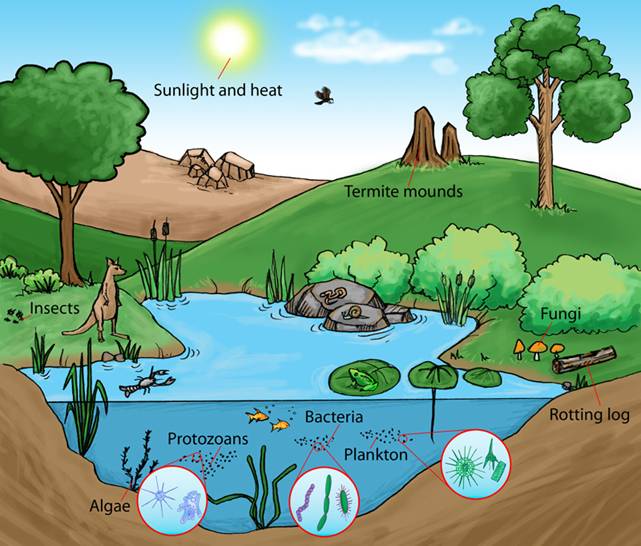
Biotic factors not only shape the savanna’s structure but also drive its ecological processes. Here’s how:
Nutrient Cycling
Decomposers like bacteria and fungi break down organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil. This process is vital for maintaining soil fertility and supporting plant growth. Nutrient cycling, soil health, and decomposer organisms are critical components of savanna ecosystems.
Competition and Symbiosis
Competition for resources among species drives adaptation and diversity. For example, different grass species evolve to thrive in specific conditions. Symbiotic relationships, such as those between ants and acacia trees, also enhance survival. These interactions illustrate the principles of ecological competition, symbiotic relationships, and species adaptation in savannas.
📌 Note: Understanding biotic factors is crucial for predicting how savannas may respond to climate change and human activities, such as deforestation and agriculture.
Summary and Checklist

In summary, biotic factors are the lifeblood of savanna ecosystems, influencing everything from vegetation patterns to wildlife behavior. Here’s a checklist to recap the key points:
- Vegetation provides habitat and food, shaping the savanna landscape.
- Wildlife interactions, such as predator-prey dynamics, maintain ecological balance.
- Decomposers drive nutrient cycling, supporting soil fertility.
- Competition and symbiosis foster biodiversity and adaptation.
By exploring these biotic factors, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and resilience of savanna ecosystems. Whether you're studying ecology, planning a safari, or advocating for conservation, understanding these dynamics is essential. Savanna conservation, ecological research, and sustainable practices are more important than ever to protect these incredible landscapes for future generations.
What are the main biotic factors in savanna ecosystems?
+The main biotic factors include vegetation (grasses and trees), wildlife (herbivores and predators), decomposers (bacteria and fungi), and symbiotic relationships between species.
How do predators affect savanna ecosystems?
+Predators regulate herbivore populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining vegetation health. This balance is crucial for the overall stability of the ecosystem.
Why is nutrient cycling important in savannas?
+Nutrient cycling ensures soil fertility by breaking down organic matter and returning essential nutrients to the soil, supporting plant growth and ecosystem productivity.