Molar Mass of BF3: Quick Calculation Guide

Calculating the molar mass of BF3 (Boron Trifluoride) is a fundamental skill in chemistry, essential for stoichiometry, solution preparation, and understanding molecular properties. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional, this guide provides a quick and accurate method to determine the molar mass of BF3. By following these steps, you’ll gain confidence in handling chemical calculations, ensuring precision in your work. (molar mass calculation, BF3 molar mass, chemical calculations)
Understanding Molar Mass: A Brief Overview

Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It’s calculated by summing the atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule. For BF3, this involves boron (B) and fluorine (F). Understanding molar mass is crucial for various applications, including chemical reactions, material science, and pharmaceuticals. (molar mass definition, atomic mass, chemical applications)
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate the Molar Mass of BF3
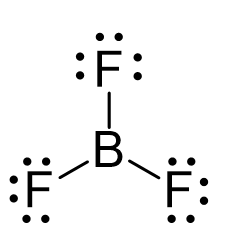
Step 1: Identify Atomic Masses
Refer to the periodic table for the atomic masses of boron (B) and fluorine (F).
- Boron (B): Approximately 10.81 g/mol
- Fluorine (F): Approximately 19.00 g/mol
📌 Note: Ensure you use precise atomic masses for accurate calculations.
Step 2: Determine the Molecular Formula
BF3 consists of one boron atom and three fluorine atoms. This formula is essential for calculating the total molar mass.
Step 3: Calculate the Molar Mass
Add the atomic masses of all atoms in the molecule:
[
\text{Molar Mass of BF3} = (1 \times \text{B}) + (3 \times \text{F})
]
[
\text{Molar Mass of BF3} = (1 \times 10.81) + (3 \times 19.00)
]
[
\text{Molar Mass of BF3} = 10.81 + 57.00 = 67.81 g/mol
]
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms | Total Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boron (B) | 10.81 | 1 | 10.81 |
| Fluorine (F) | 19.00 | 3 | 57.00 |
| Total Molar Mass of BF3 | 67.81 | ||
Practical Applications of BF3 Molar Mass

Knowing the molar mass of BF3 is vital for:
- Stoichiometry: Balancing chemical equations accurately.
- Solution Preparation: Determining the amount of BF3 needed for a specific concentration.
- Material Science: Understanding the properties of boron-based compounds.
Checklist for Molar Mass Calculation

- [ ] Gather atomic masses from the periodic table.
- [ ] Identify the molecular formula of the compound.
- [ ] Multiply atomic masses by the number of atoms.
- [ ] Sum the values to obtain the molar mass.
The molar mass of BF3 is 67.81 g/mol, calculated by summing the atomic masses of boron and fluorine. This guide provides a straightforward method for accurate calculations, essential for various chemical applications. Mastery of this skill ensures precision in laboratory work, research, and industrial processes. (BF3 molar mass, molar mass calculation, chemical precision)
What is the molar mass of BF3?
+
The molar mass of BF3 is 67.81 g/mol.
Why is molar mass important in chemistry?
+
Molar mass is crucial for stoichiometry, solution preparation, and understanding molecular properties in chemical reactions.
How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound?
+
Sum the atomic masses of all atoms in the compound, considering the number of each atom in the molecular formula.



