Cell Nucleus Analogy: The Brain Inside Your Cell's Control Center

Imagine a bustling city, with each building serving a specific function – factories, offices, power plants, all working together to keep the city running smoothly. Now, shrink that city down to the microscopic level, and you have a cell, the fundamental unit of life. Within this cellular city, the cell nucleus acts as the central command center, much like a city hall, directing all activities and ensuring everything functions harmoniously.
The cell nucleus is often referred to as the “brain” of the cell, and for good reason. It houses the cell’s DNA, the genetic blueprint that contains instructions for growth, development, and reproduction. Without the nucleus, the cell would be like a city without a government – chaotic and unable to sustain itself.
The Role of the Cell Nucleus: Directing Cellular Operations
The cell nucleus plays a critical role in maintaining cellular functions. It regulates gene expression, controls cell division, and ensures the cell responds appropriately to its environment. Think of it as the CEO of a company, making high-level decisions that impact every department.
- DNA Storage: The nucleus safeguards the cell’s DNA, protecting it from damage and ensuring its accurate replication during cell division.
- Gene Expression: It determines which genes are turned on or off, influencing protein synthesis and cellular activities.
- Cell Cycle Control: The nucleus oversees the cell cycle, deciding when the cell should grow, divide, or even self-destruct if necessary.
📌 Note: The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the nucleus, ensuring its integrity.
Cell Nucleus Analogy: Simplifying the Complexity

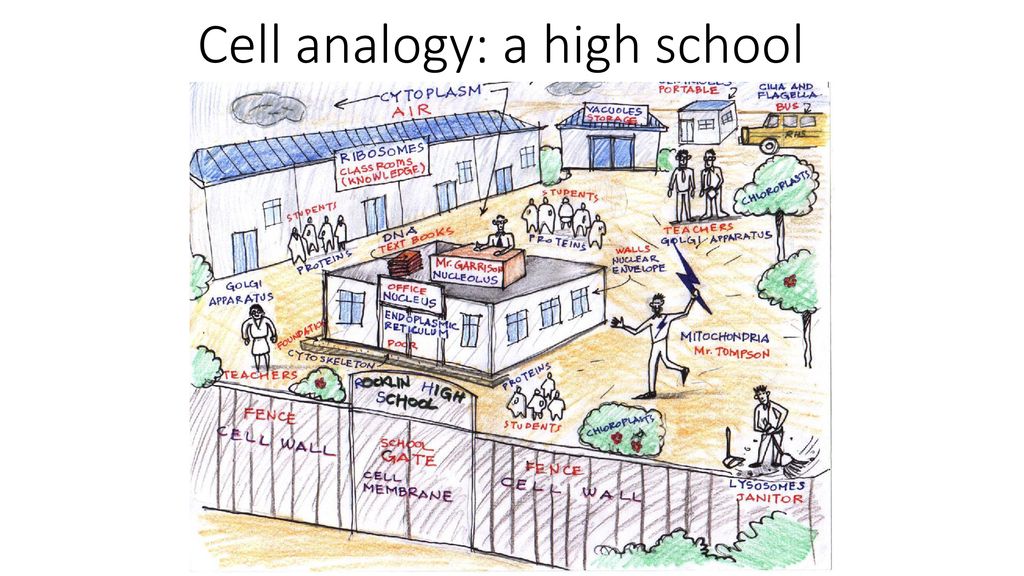
To better understand the nucleus, let’s use an analogy: the cell is a factory, and the nucleus is the manager’s office.
| Cell Component | Factory Analogy |
|---|---|
| Cell Nucleus | Manager’s Office (Decision-Maker) |
| DNA | Blueprint for Products |
| Cytoplasm | Factory Floor (Work Area) |
| Ribosomes | Assembly Line Workers |

Just as the manager’s office directs operations, the nucleus controls the cell’s activities, ensuring everything runs efficiently.
Why the Cell Nucleus Matters in Health and Disease

Understanding the cell nucleus is crucial in fields like medicine and biotechnology. Abnormalities in the nucleus can lead to diseases such as cancer, where cells divide uncontrollably. Researchers study the nucleus to develop targeted therapies that can correct these issues.
For commercial-intent visitors, products like nuclear staining kits and advanced microscopy tools are essential for studying the nucleus in detail. These tools enable scientists to visualize and analyze nuclear structures, paving the way for breakthroughs in research and diagnostics.
Key Takeaways: The Cell Nucleus in a Nutshell
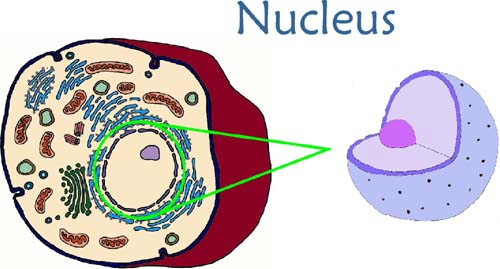
- The cell nucleus is the control center of the cell, housing DNA and regulating cellular activities.
- It plays a vital role in gene expression, cell division, and maintaining cellular health.
- Analogies like the “manager’s office” simplify its complex functions, making it easier to understand.
- Research on the nucleus has significant implications for health, disease, and biotechnology.
What is the main function of the cell nucleus?
+The cell nucleus primarily stores DNA, regulates gene expression, and controls the cell cycle, acting as the cell's command center.
How does the nucleus protect DNA?
+The nucleus is enclosed by a nuclear envelope, which shields DNA from damage and regulates the entry and exit of molecules.
Why is the nucleus compared to the brain of the cell?
+The nucleus is likened to the brain because it contains the cell's genetic information and directs all cellular activities, much like the brain controls the body.
In summary, the cell nucleus is the unsung hero of cellular function, ensuring the cell operates seamlessly. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional, understanding the nucleus opens doors to appreciating the intricacies of life itself. (cell biology, genetic research, biotechnology advancements)



